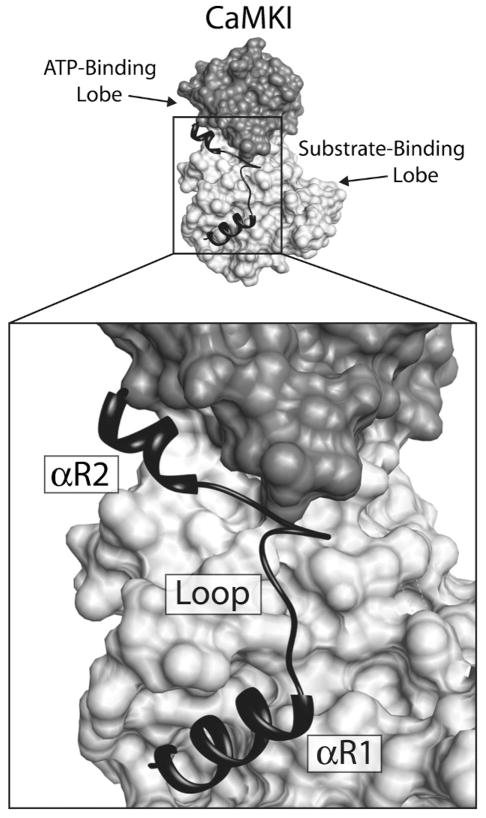
Figure 7.
Interactions of the CaMKI regulatory domain with the catalytic core. Depicted above is a surface rendering of CaMKI with a ribbon diagram of the regulatory domain lying across the face of the molecule. The ATP-binding lobe of the catalytic core is colored dark gray and the substrate-binding domain is light gray. The regulatory domain, which contains both the autoinhibitory and CaM-binding domains, is black. The structure of the regulatory domain is composed of two regulatory helices (αR1 and αR2) connected by a loop. Regulatory helix αR1 makes contacts with the substrate binding domain, blocking interactions with substrate, and αR2 inhibits ATP binding through interactions with residues in the ATP-binding domain.