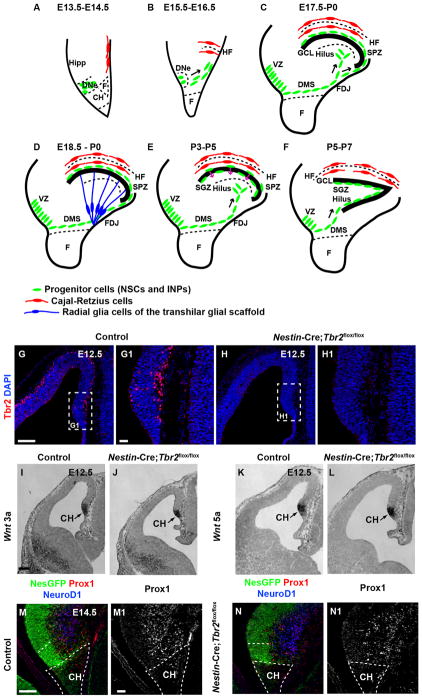
Figure 1. Early development of the DG is essentially normal in Nestin-Cre;Tbr2flox/flox mice.
(A–F) Schematic diagram illustrating the steps in DG development. Progenitor cells (NSCs and INPS) are shown in green. Cajal-Retzius cells are shown in red. The transhilar radial glial scaffold is shown in blue. (A–B) Progenitor cells initially located in the dentate neuroepithelium (DNe) migrate to the primordial DG concurrent with invagination of the pial surface and migration of Cajal-Retzius cells to the hippocampal fissure (HF) between E13.5 and E16.5. (C) Continued migration of progenitors through the dentate migratory stream (DMS) contributes to formation of the subpial neurogenic zone (SPZ) during later stages of development (E17.5-P0). (D) The transhilar radial scaffold forms at approximately the same time as radial glia become localized to the fimbriodentate junction (FDJ). (E) Transition of progenitor cells out of the SPZ occurs between P3–P5. (F) The subgranular zone (SGZ) neurogenic niche is established by P5–P7. (G-G1) Tbr2 protein (red) is expressed in cells in the cortical hem (CH) at E12.5 in control mice. (H-H1) Tbr2 protein is ablated in the cortical hem of mutant mice by E12.5. White dashed boxes in G and H represent areas shown at higher magnification in G1 and H1, respectively. (I–L) Expression of Wnt3a and Wnt5a, markers of the cortical hem, are present at approximately normal levels in Nestin-Cre;Tbr2flox/flox mice. (M–N, M1-N1) Markers of DG granule neurons (NeuroD1, Prox1) are present in the primordial DG of mutant mice, but are slightly reduced in comparison to controls as early as E14.5. Scale bars: G = 100 μm, G1 = 20 μm, I = 100 μm, M = 75 μm, M1 = 15 μm.