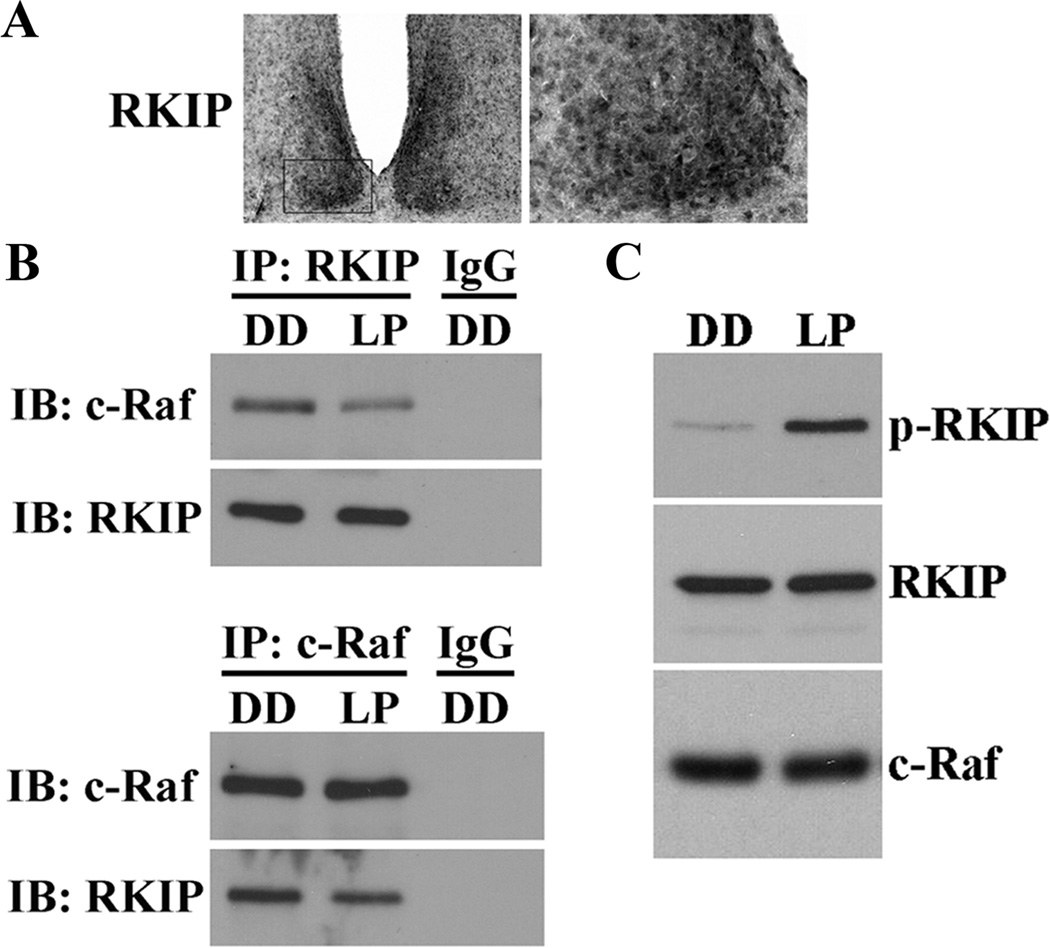
Figure 1. Light induces the phosphorylation of RKIP and its dissociation from c-Raf in the SCN.
A, Representative micrographs of total RKIP expression in the murine SCN at ZT 8. Boxed region (left) is shown in high magnification on the right. B, Light-responsive interaction between RKIP and c-Raf in the SCN as determined by co-IP. Mice received a 15 min light pulse (LP: 400 lux intensity) at CT 15 and were killed 5 min later. Control mice were killed at the same circadian time without receiving a light pulse (DD). SCN protein extracts were immunoprecipitated (IP) with antibodies against total RKIP (top) or total c-Raf (bottom) and immunoblotted (IB) with both antibodies. IP with rabbit IgG was used as a negative control. A brief light pulse in the early subjective night reduces the binding interaction of RKIP and c-Raf. C, Light-induced phosphorylation of RKIP as determined by Western blot analysis. Mice received a 15 min light pulse (LP: 400 lux intensity) at CT 15 and were killed 5 min later. Control mice were killed at the same circadian time without receiving a light pulse (DD). Blots were probed with antibodies against the Thr-153-phosphorylated form of RKIP (p-RKIP) (top), total RKIP (middle), and total c-Raf (bottom). Light triggers rapid and robust phosphorylation of RKIP at Thr-153 in the SCN.