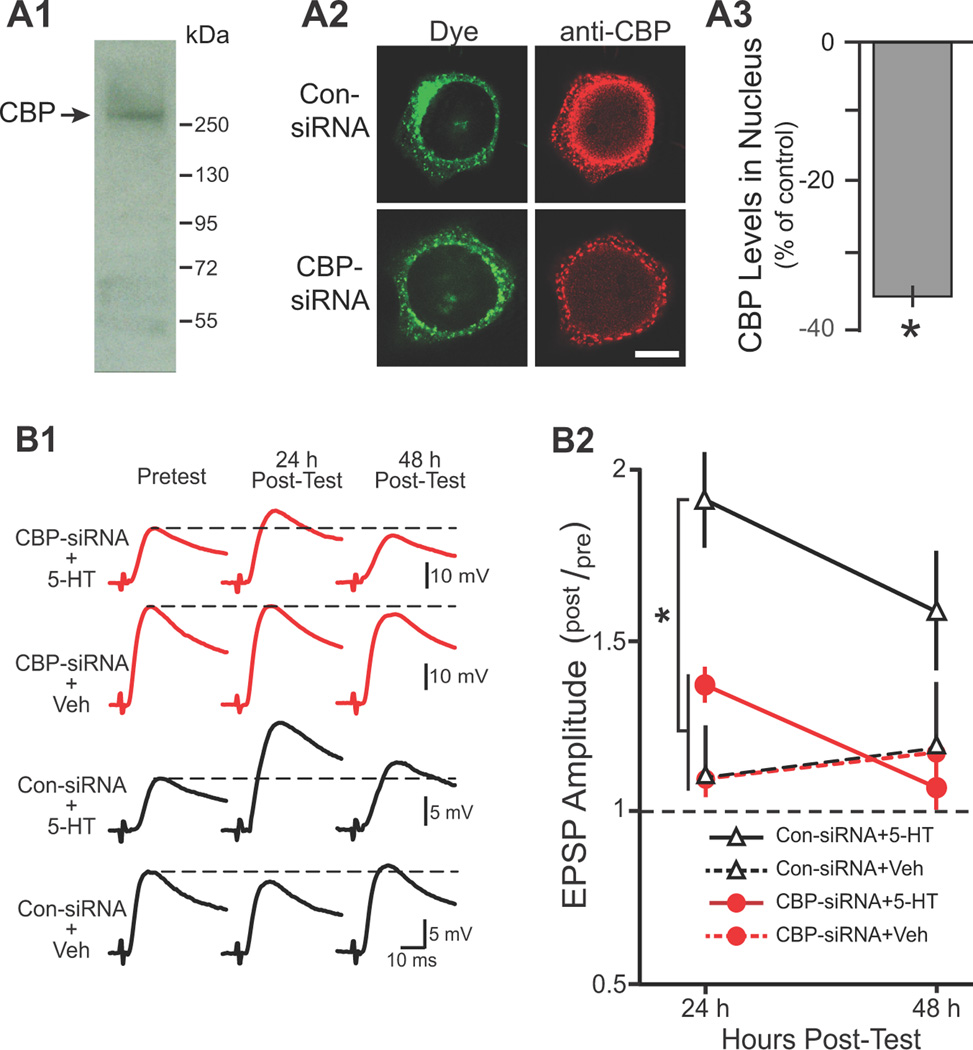
Figure 1. CBP-siRNA reduced the nuclear levels of CBP and impaired LTF.
A1, Western blot analysis of nuclear extracts from Aplysia CNS revealed a single band with a molecular weight appropriate for CBP. A2, Representative confocal images of CBP immunofluorescence in SNs 96 h after injection with either control siRNA (Con-siRNA) or CBP-siRNA. Fluorescein dye was co-injected to verify that SN cytoplasm and processes (but not the nucleus) were filled. Scale bar, 20 µm. A3, Summary data. CBP levels in the nucleus of SNs were significantly reduced 96 h after injection with CBP-siRNA as compared to SNs injected with Con-siRNA. B1, Representative EPSPs recorded immediately before (Pretest) and 24 and 48 h after (Post-test) the Standard Protocol. Dashed lines represent the amplitude of the Pretest EPSP. B2, Summary data. Synaptic plasticity was measured as the ratio of post-test to pretest EPSPs (post/pre). Significant differences among treatment groups are indicated by * (indicates P < 0.05).