Fig. 3. Arm-type site protection patterns in the integrative recombination HJ intermediate.
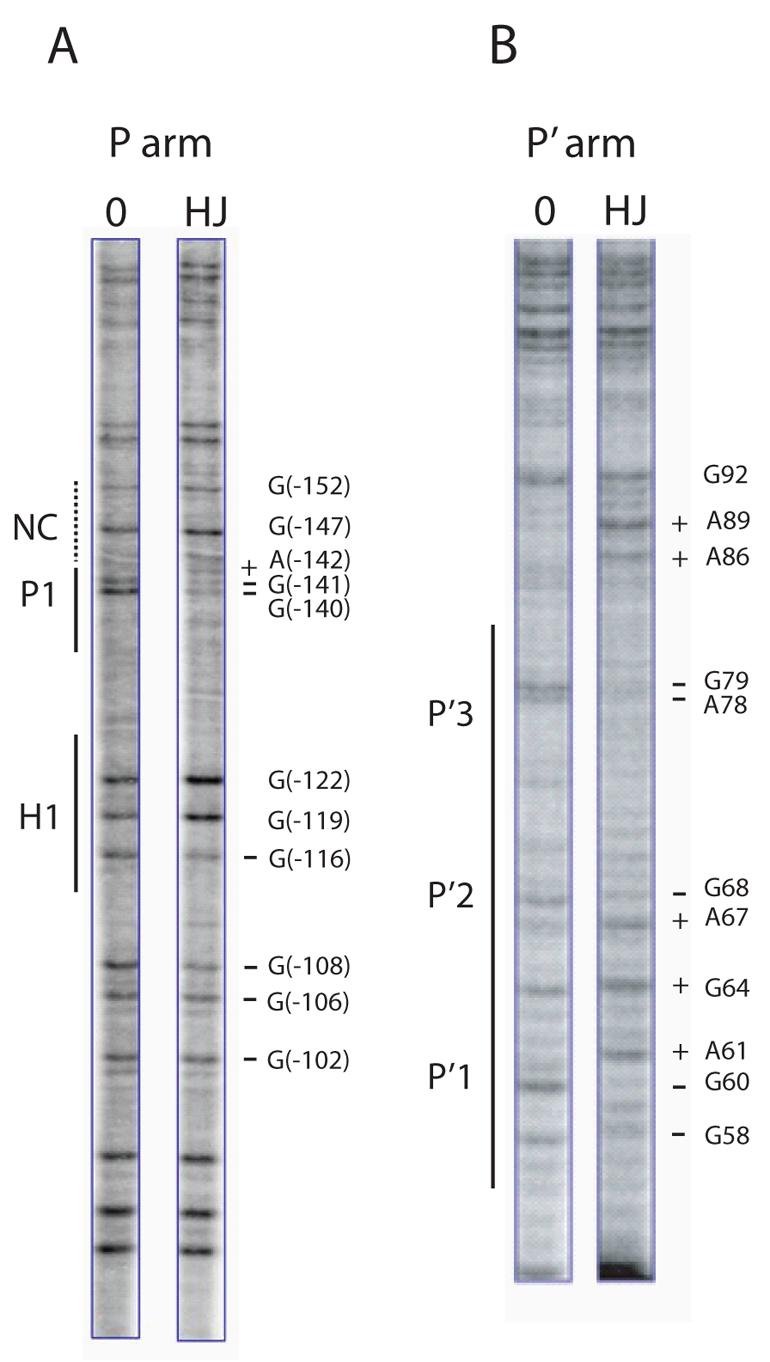
DMS protection patterns of arm-type sites in the P arm (A), and P′ arm (B), of the integrative HJ recombination intermediate. Following recombination between attP and attB in the presence of the peptide, the DNAs were treated with DMS and the HJ was purified by gel electrophoresis. A uniquely end-labeled fragment of the P or P′ arm was generated by subjecting the supercoiled HJ complex to an appropriate sequence of restriction digests and end-labeling reactions (see Experimental Procedures). Cleavage of DNA at the methylated bases was followed by gel electrophoresis and autoradiography. The minus protein control lanes (0) were generated by a similar treatment of a supercoiled attP without the addition of recombination proteins. As a result of the digestion and labeling strategy, the H′ site is not visible in the footprints of the P′ arm in (B). The predicted location of the putative non-canonical site is denoted by the NC label and a dashed line in (A). Coordinates for the sites of significantly diminished (−) and enhanced (+) cleavage refer to the standard numbering of the attP sequence (14,52).
