Fig. 4. Biotin Interference Assay (BIA) of Int arm-type site interactions.
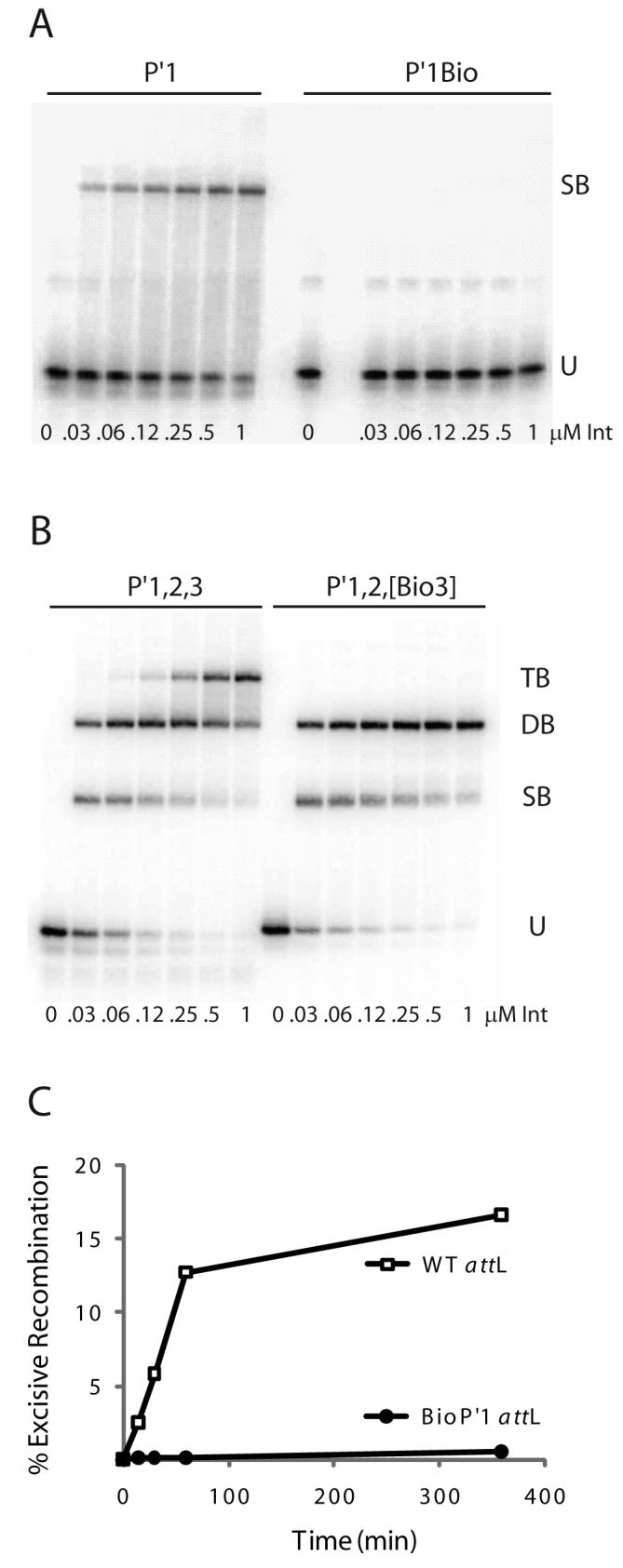
A. Increasing concentrations of Int were used in gel mobility shift binding assays with a 33 bp radiolabeled oligonucleotide encoding the P′1 arm-type site (P′1) and the same fragment containing a biotin dT substitution in P′1 (P′1Bio) at position 4 in the top strand of the arm-type site consensus sequence (10): U, unbound substrate, SB, singly-bound substrate. B. Gel mobility shift binding assays with a 50 bp radiolabeled oligonucleotide encoding the P′1,2,3 arm-type sites (P′1,2,3) and the same fragment containing biotin dT substitutions (P′1,2,[Bio3]) at position 4 in the top strand and position 6 in the bottom strand arm-type site consensus sequence: U, SB, DB, and TB; unbound, singly-, doubly-, and triply-bound substrate, respectively. C. Biotin Interference Assay of excisive recombination between attR and attL (WT) or an attL with a biotin dT insertion (P′1Bio) at the bottom strand T at position 6 of P′1.
