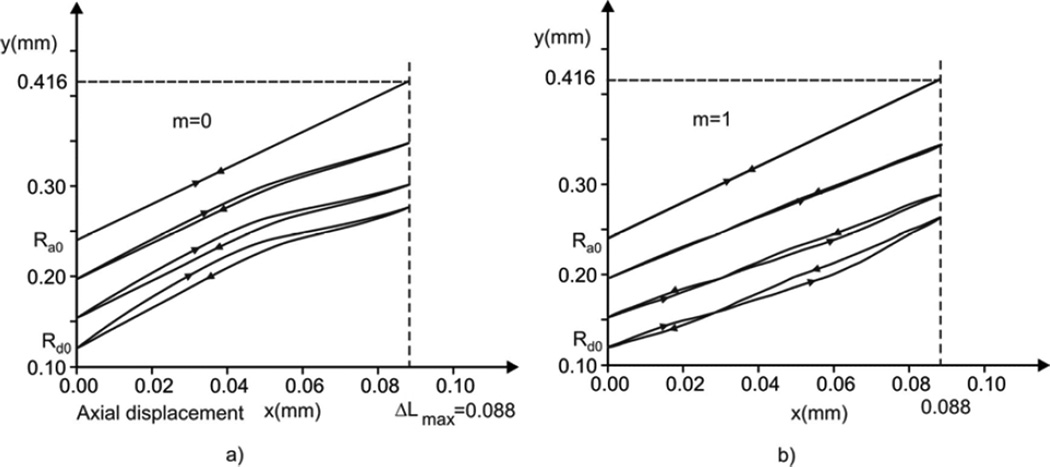
Figure 7.
Particle trajectories within radial plane (x-y) of material points at outer boundary, internal rim and at two membrane radii. Axial maximum displacement is (ΔL)max = 0.5 (ΔRd)max following form geometrical similarity during alveolar deformation (see equation 1). a) Case with no muscle constituent (m = 0): the trajectories display clockwise hysteretic loops due to dominant surfactant action during inspiration (see Fig. 2d), with loops diminishing from the internal to the external membrane boundary; b) Case m = 1: The muscle hysteresis acts in the opposite sense form the surfactant effects (see Fig. 2c), and hysteretic loops become counterclockwise in the regime where muscle hysteretic effect is dominant (expiration regime); the loops diminish when approaching to external boundary.