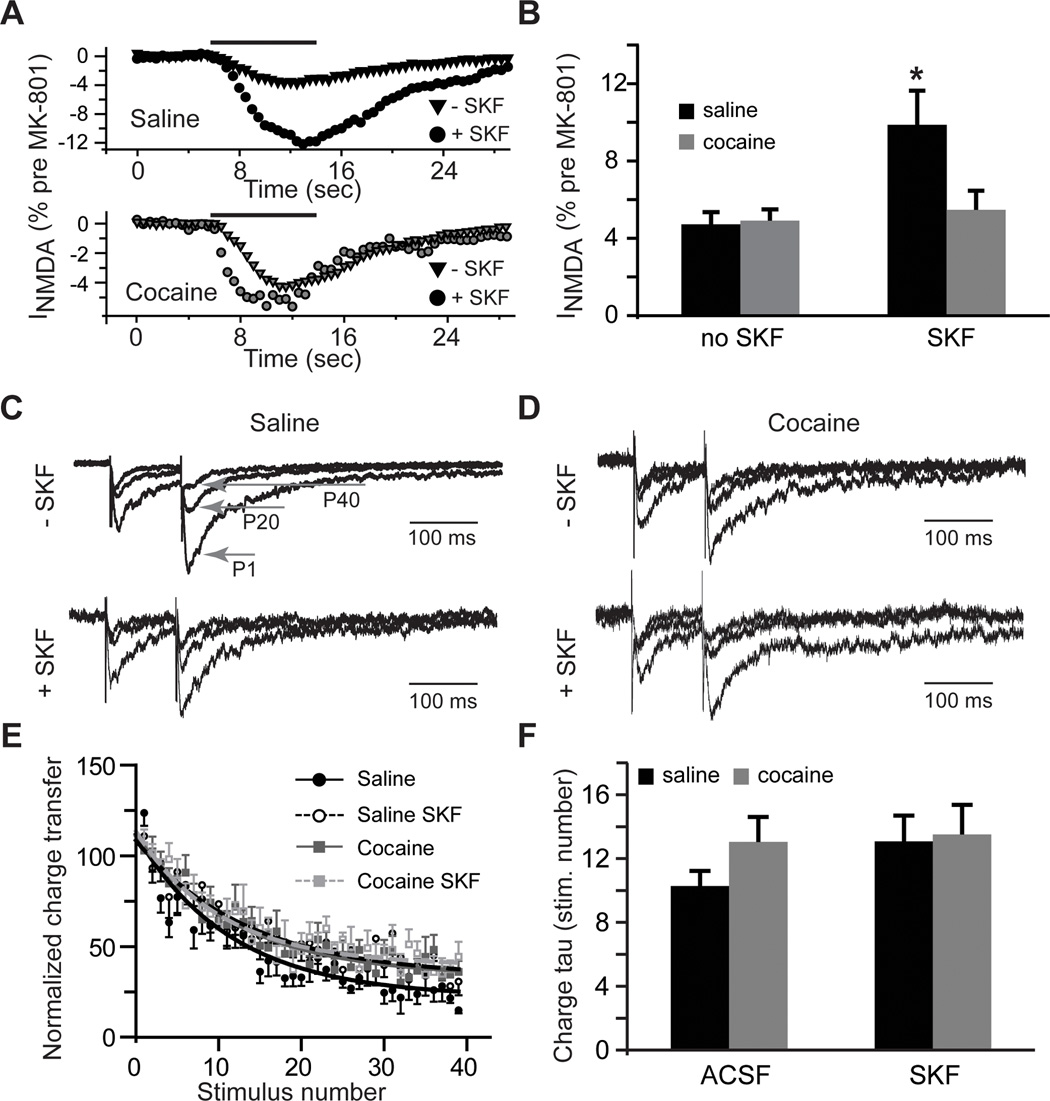
Figure 2. Extrasynaptic NMDAR-mediated currents increase following D1DR stimulation.
A) Time-course of whole-cell NMDA (100 µM, solid black line) responses after blockade of synaptic NMDARs by MK-801 (40 µM) is expressed as a fraction of whole-cell NMDA responses measured before MK-801 application. B) Bar histograms illustrating an increase in extrasynaptic NMDAR-mediated currents in slices from cocaine-naïve rats following D1DR stimulation (t(11)=2.54; *, p<0.05 vs. saline no SKF; n=6–11 cells). C) and D) Current responses to the 1st (P1), 20th (P20) and 40th (P40) stimulation pulses illustrate use-dependent block of NMDA eEPSCs by MK-801across the experimental groups. Current amplitudes are normalized to the first eEPSC in the saline no SKF group for ease of comparison. E) A summary of the time-course of synaptic responses in the presence of MK-801 illustrates a slight increase in the rate of MK-801 block in the saline group. F) Bar histograms summarizing the rate of block (expressed as stimulation pulse number) by MK-801.