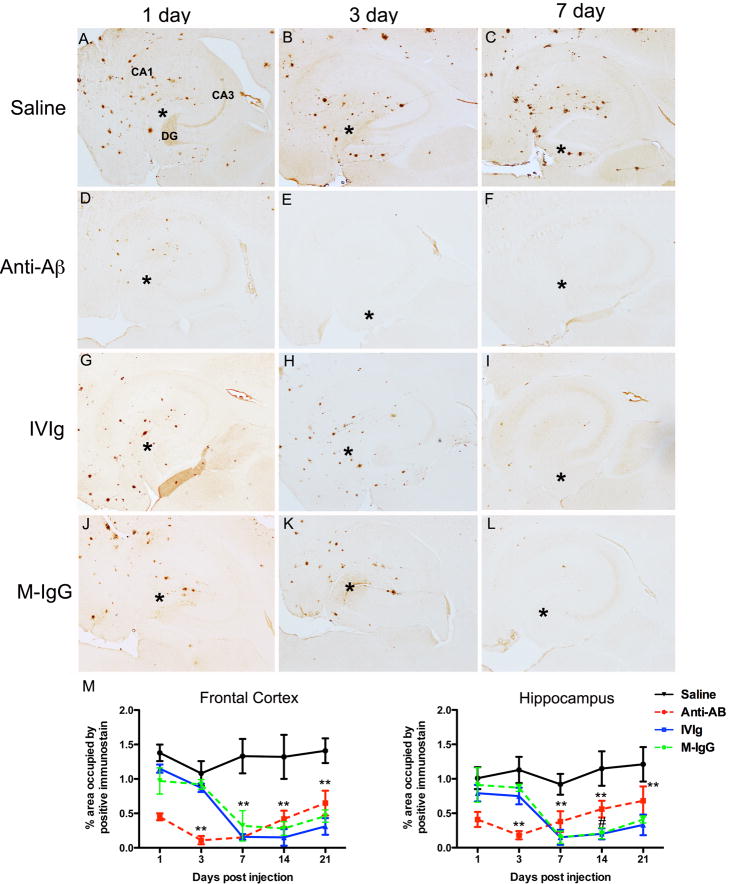
Figure 2.
Brain Aβ is reduced by anti-Aβ antibodies, IVIg and mouse IgG. Panels A-C show the hippocampus of mice receiving saline 1 (A), 3 (B) and 7(C) days following injection. Panels D-F show the hippocampus of mice receiving anti-Aβ antibody 1 (D), 3 (E) and 7 (F) days following injection. Panels G-I show the hippocampus of mice receiving IVIg 1 (G), 3 (H) and 7 (I) days following injection. Panels J-L show the hippocampus of mice receiving mouse IgG 1 (J), 3 (K) and 7 (L) days following injection. In Panel A, the dentate gyrus (DG), cornu ammonis 3 (CA3) and cornu ammonis 1 (CA1) regions are indicated to provide orientation. Asterisks in panels A-L indicate the injection site within the hippocampus. Panels M and N show quantification of Aβ across the full time-course, from 1 to 21 days, in the frontal cortex (M) and hippocampus (N). ** indicates P<0.01 compared to saline for all points under the asterisk. # indicates P<0.05 for IVIg and mouse IgG compared to anti-Aβ antibody.