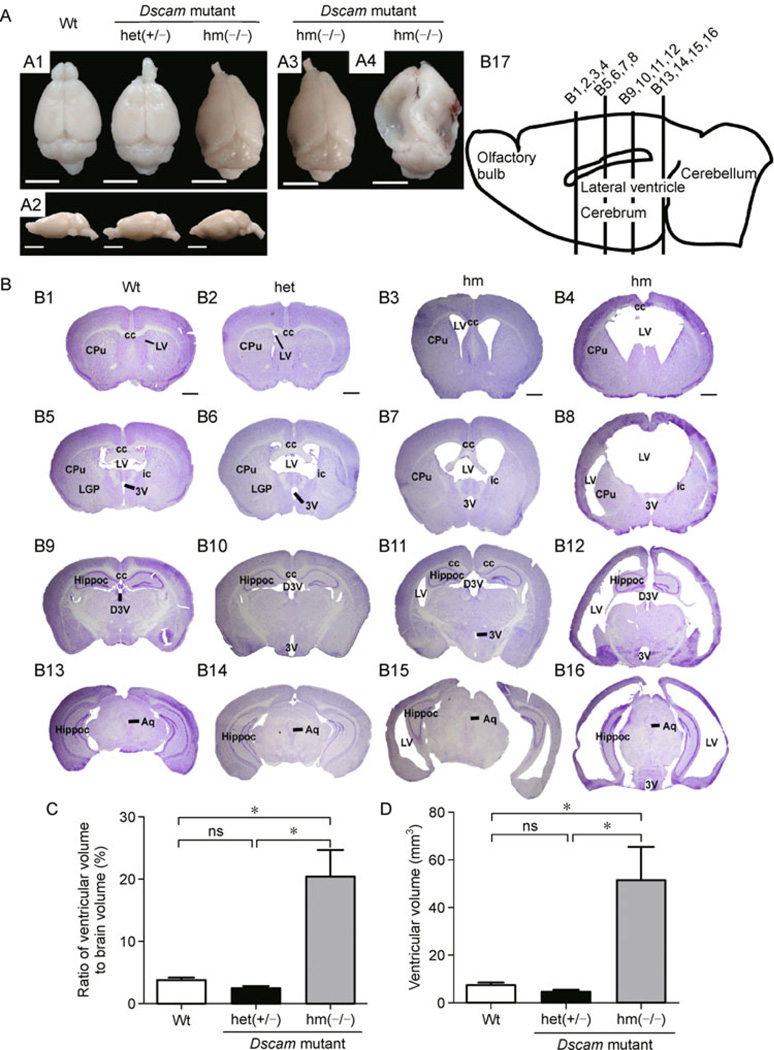
Figure 3. Hydrocephalus in homozygous Dscamdel17 mutant mice.
(A) From the dorsal (A1) and lateral (A2) views, homozygous Dscamdel17 mutant mice brains show significant deformation with collapsed cortices in the caudal region and smaller olfactory bulbs. The degree of brain tissue collapse varies among different individual mice. Two out of five brains (A3) showed mild changes in the caudal region, whereas other three brains (A4) exhibited severe collapse from the middle to caudal regions (scale bars: 0.5 cm). (B) Coronal sections of brains were stained using Nissl staining. Coronal section of the wild type mice (B1, B5, B9, and B13) and heterozygous Dscamdel17 mutant mice (B2, B6, B10, and B14) showed normal ventricles, whereas age-matched homozygous Dscamdel17 mutant mice (B3, B4, B7, B8, B11, B12, B15, and B16) exhibited enlarged cerebral ventricles, a progressively-thinned cortical mantle, and stretched internal capsule fibers at different rostrocaudal levels. Different homozygous Dscamdel17 mutant mice showed different degrees of ventricular enlargement (B3, B4, B7, B8, B11, B12, B15, and B16). (B17) A diagram illustrating the mouse brain and positions of four different coronal sections (scale bar, 1 mm; cc, corpus callosum; CPu, caudate putamen (striatum); LV, lateral ventricle; LGP, lateral globus pallidus; ic, internal capsule; 3V, 3rd ventricle; Hippoc, Hippocampus; D3V, drosal 3rd ventricle; Aq, aqueduct). (C and D) Comparison of ventricular size. Compared with wild type and heterozygous Dscamdel17 mutant mice, homozygous Dscamdel17 mutant mice showed significant increases in the ventricular volume, either measured by the ratio of ventricular to total brain volumes (panel C, means ± SEM, One-way ANOVA and Bonferrioni’s multiple comparison test, *p < 0.05; ns, no significance) or as absolute ventricular volumes (panel D) [Wt, wild type; het (+/−), heterozygous Dscamdel17 mutant mice; hm(−/−), homozygous Dscamdel17 mutant mice].