Figure 4. Role of GRK5 on bacterial load following cecal ligation and puncture.
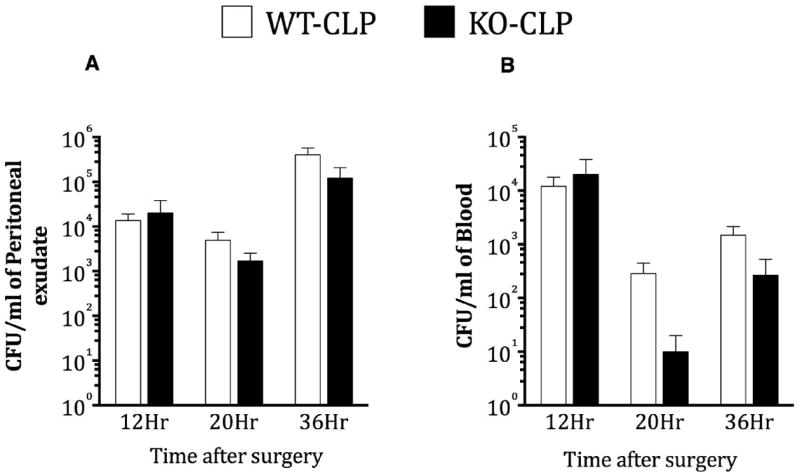
Blood and peritoneal samples from GRK5 wild type and knockout mice subjected to sham or CLP surgery were assessed for bacterial load as described in the methods. CFU counts from peritoneal (A), and blood (B) for different time points are shown from mice subjected to CLP. (N= 11-14 per genotype at 12 hour time point; N= 5 per genotype at 20 hour time point; N= 9-12 for 36 hour time point). Note that sham mice did not show any bacterial colonies (data not shown).
