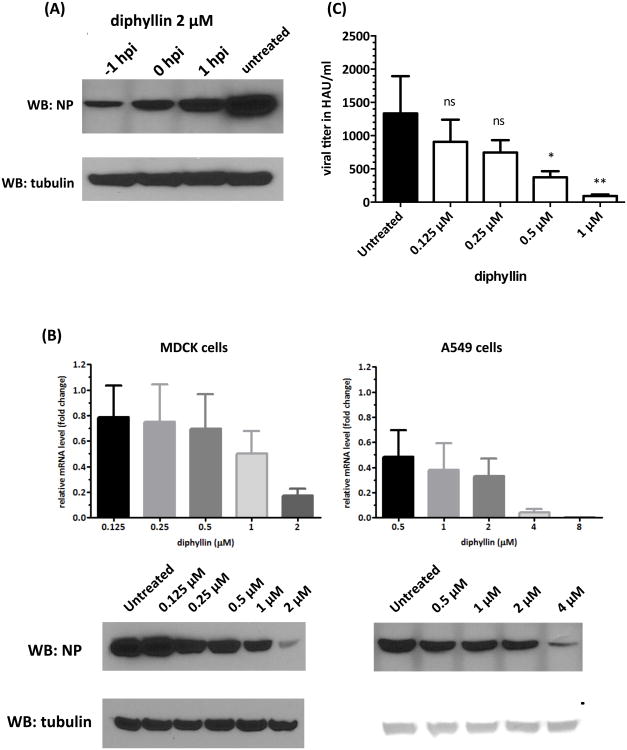
Fig. 3. Pretreatment/Treatment with diphyllin alters the cellular susceptibility to influenza virus and showed an antiviral activity against influenza virus.
(A) Two μm of diphyllin was added to MDCK cells at three different time points relative to NS1-GFP virus infection (MOI = 0.01): one hour prior to infection (-1 hpi), same time as infection (0 hpi) or one hour after infection (1 hpi). Infected cells without diphyllin treatment were used as controls. After a 1-hour infection period, all test cells were washed and incubated with fresh media containing 2 μM of diphyllin and incubated for 24 hours. Cells were then harvested and the expression of viral NP and tubulin was detected by western blotting. (B) Various concentrations of diphyllin were added to MDCK cells (left panel) or A549 cells (right panel) one hour before the NS1-GFP virus infection (MOI = 0.01). Infected cells without diphyllin treatment were used as controls. After a 1-hour period of infection, cells were washed, overlaid with fresh media containing the same concentrations of diphyllin as in previous step, and incubated for another 24 hours. Cells were lysed and the mRNA level of viral matrix gene relative to cellular β-actin was determined by quantitative RT-PCR. Results were presented as fold change of untreated control (upper panel). Expression of intracellular viral NP and tubulin was detected by western blotting (lower panel). (C) Extracellular viral titers in culture supernatant were determined with HA tests. Values are mean ± SD from three replicates. Viral titers between each treated group and the untreated control group were compared by one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's multiple comparisons test. (ns: non-significant, *: p<0.05, **: p<0.01)