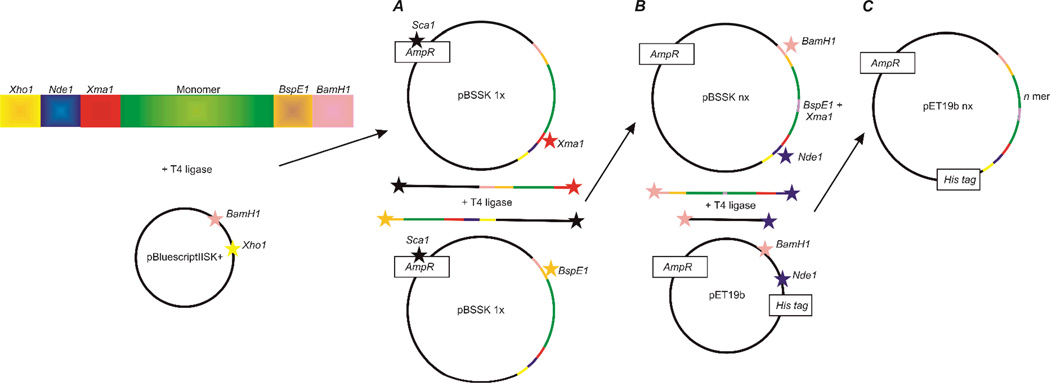
Figure 4.
Cloning strategy used by the Lewis group to engineer long repetitive spider silk sequences (in green). (A) Cloning of a silk monomer into the vector pBluescript II SK+. (B) The resulting plasmid is double digested and fragments containing silk monomers are ligated again to produce longer sequences. (C) The synthetic spider silk multimer is ligated into pET19b expression vector. Note: Restriction digestion sites are indicated by star. Adapted from reference (Teule, et al., 2009).