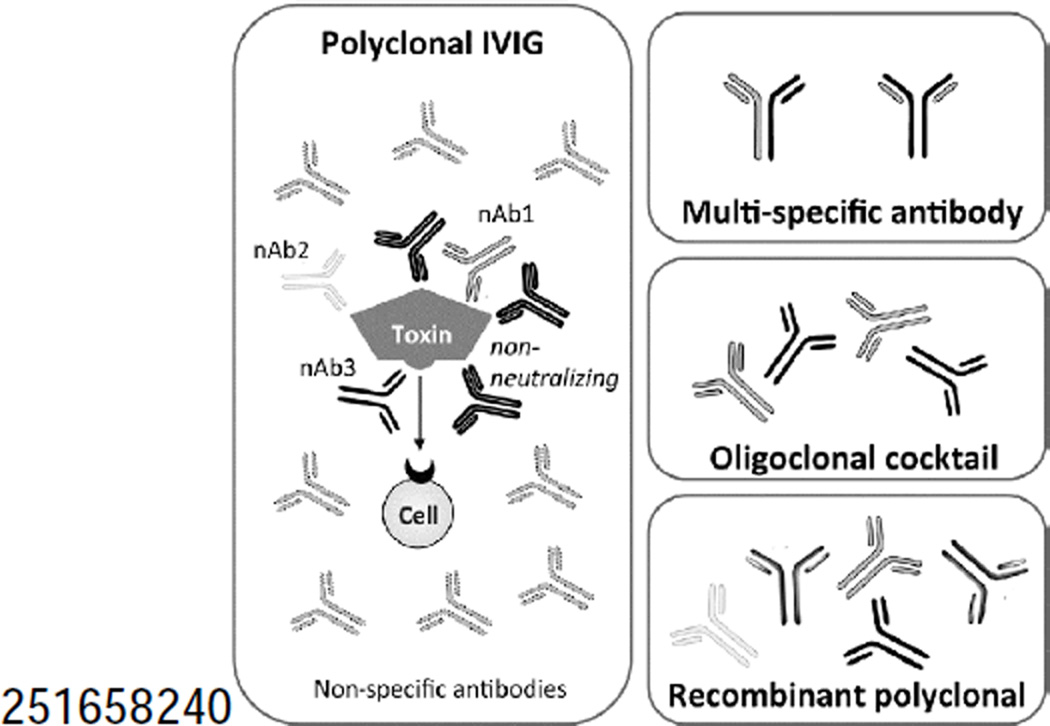
Figure 1. Polyclonal antibody therapeutics.
A, While a traditional IVIG product contains a large number of antibodies binding a variety of antigens, only a fraction bind the antigen of interest (e.g., a bacterial toxin) and of those, only a fraction are clinically relevant protective antibodies (pAb, e.g., those that competitively inhibit a toxin-receptor interaction, block toxin endocytosis or catalysis). IVIG thus requires large doses for efficacy. B, Multi-specific antibodies yield a single molecular entity able to bind two distinct epitopes, thereby combining the ease of monoclonal antibody manufacturing with broader antigen specificity. C, Oligoclonal antibody cocktails are a combination of several monoclonal antibodies, each grown, purified and characterized in parallel before combining. D, Recombinant polyclonal antibodies are comprised of multiple (two to 26) molecular entities, each binding clinically relevant epitopes. These are produced and purified en masse from a single cell line (Crucell/ Merus) or a polyclonal master cell bank (Symphogen).