FIGURE 8. Comparisons of steroid binding modes in catalysis.
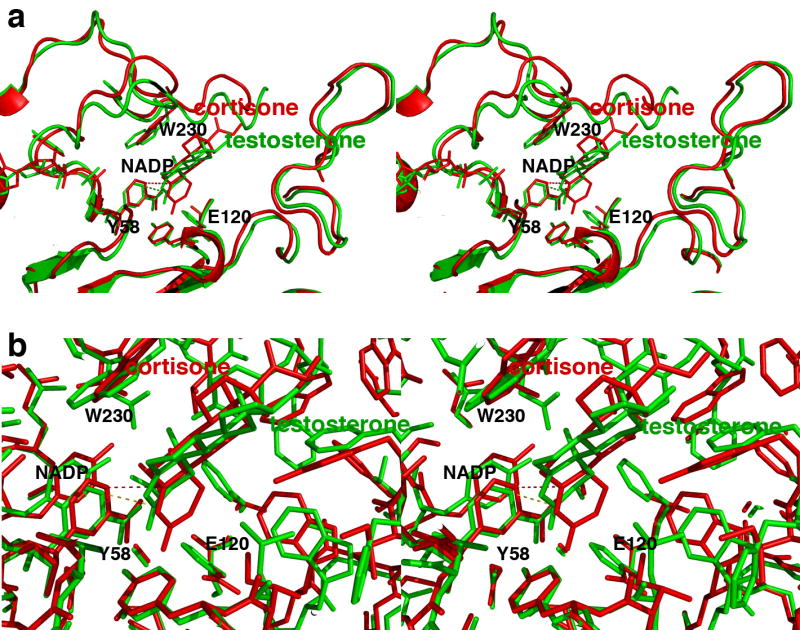
(a) Superposition of the AKR1D1-NADP+-cortisone complex (red) on the AKR1C9-NADP+-testosterone complex (green) showing that the A ring of the substrate binds ∼1 Å deeper in the active site of the former enzyme relative to the position of the nicotinamide ring of NADP+. Presuming that NADPH binds similarly to NADP+, the 4-pro-R hydride of NADPH would be adjacent to the substrate C3 carbonyl carbon in the AKR1C9 active site (green dotted line), whereas the 4-pro-R hydride of the NADPH cofactor would be adjacent to C5 of the substrate carbon-carbon double bond in the AKR1D1 active site (red dotted line). (b) Same orientation as (a), but a close-up view showing all atoms.
