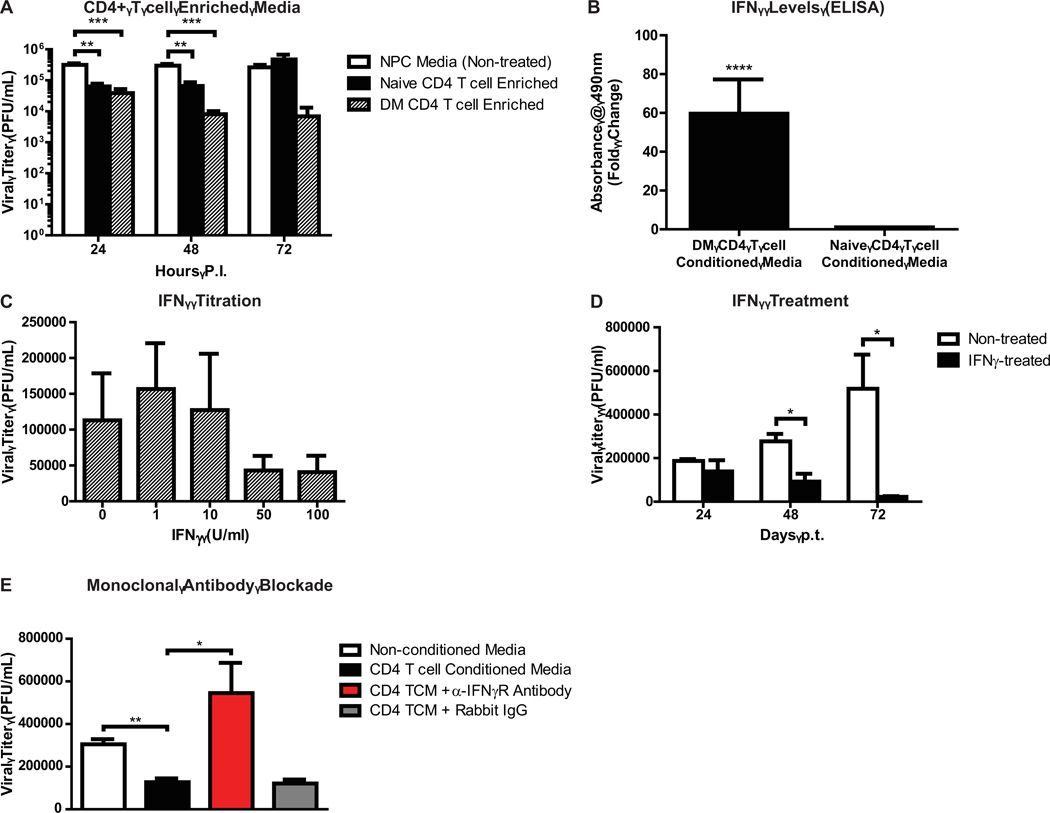
Figure 5. Virus-specific CD4+ T cell enriched media reduces viral titers via IFN-γ.
(A) Media enriched with cytokines from naïve or CD4+ T cells significantly (p < 0.01 and p < 0.001, respectively) reduced viral titers in JHMV-infected NPCs at defined times p.i. compared to non-conditioned media. (B) Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for IFN-γ in naïve-versus-DM-specific CD4+ T cell supernatants. Absorbance values at 490nm were normalized to media alone and expressed as fold changes (DM absorbance / naïve absorbance). For statistical analysis, background-subtracted absorbance values were used (****p < 0.0001). (C) High doses of IFN-γ suppress JHMV replication in NPCs, and (D) treatment with 100 U/mL IFN-γ significantly inhibits virus replication at 72 hours p.t. (E) Monoclonal antibody blockade of IFN-γ receptor abrogated the virus-suppressive effects of DM CD4+ T cell conditioned media. For all panels, data is presented as average ± SEM and represents 3 independent experiments (*p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001).