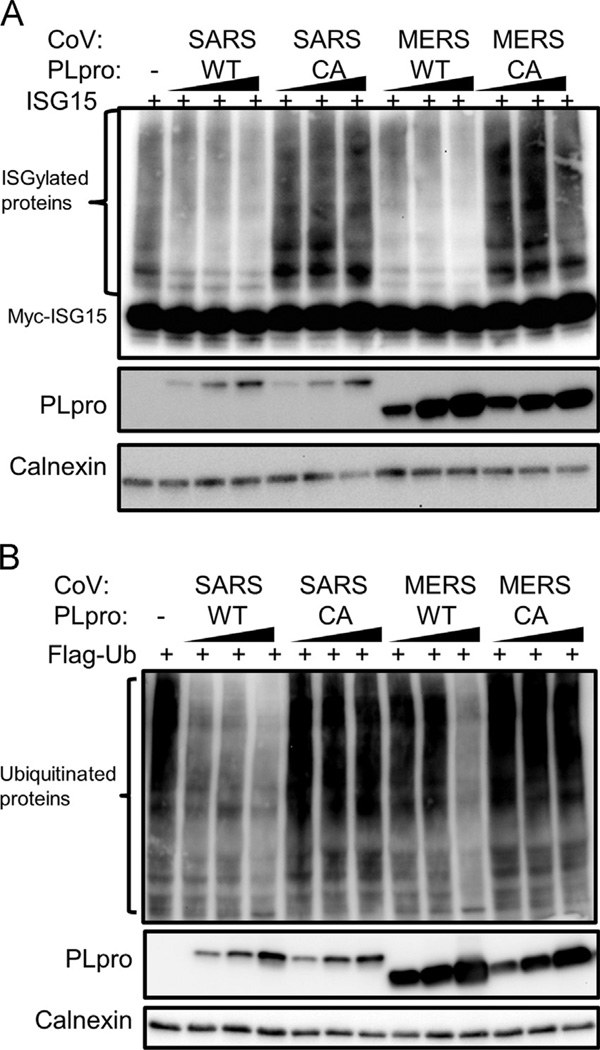
Fig. 2.
Enzymatic activites of SARS-CoV PLpro and MERS-CoV PLpro. (A) deISGylating activity of SARS-CoV PLpro and MERS-CoV PLpro, HEK293T cells were transfacted with myc-ISG15, E1, E2, E3 ISGylating machinery plasmids, and wild type (WT) or catalytic mutant (CA) PLpro expression plasmids. At 18 h post-transfection, cells were lysed and analyzed by western blotting. (B) Deubiquitinating activity of SARS-CoV PLpro and MERS-CoV PLpro. HEK293T cells were transfected with Flag-Ub expression plasmid, and wild type (WT) or catalytic mutant (CA) PLpro. Cells were lysed 18 h post-transfection and analyzed by western blotting. Figure shows representative data from at least two independent experiments.