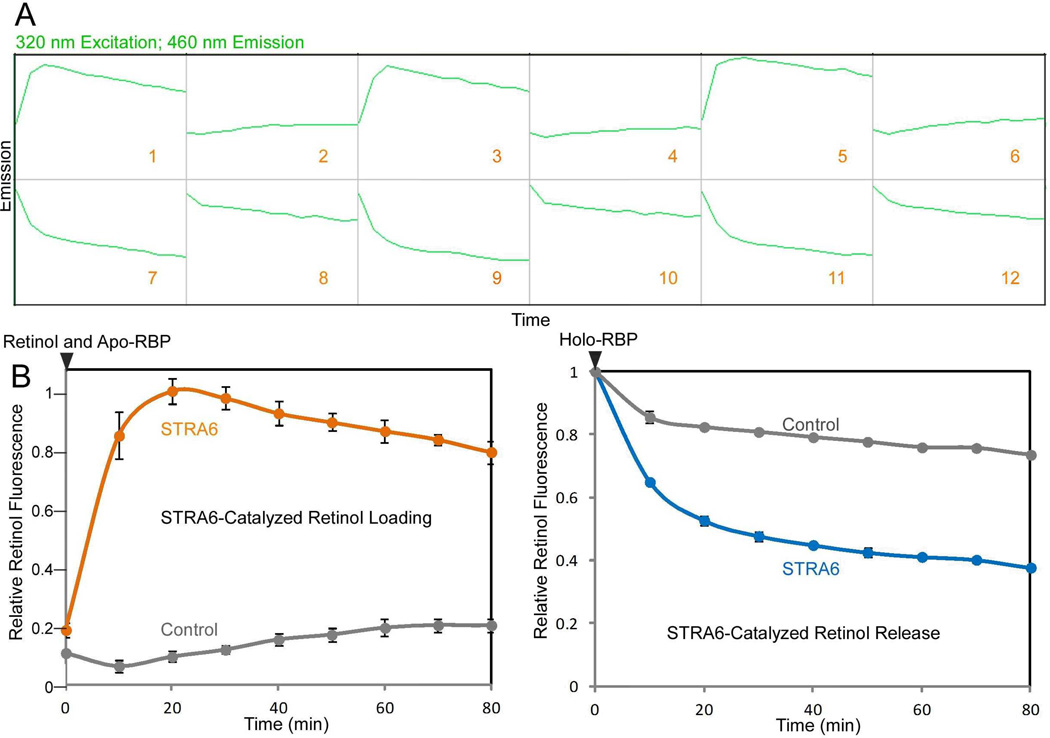
Figure 2.
Real-time monitoring of STRA6-catalyzed retinol loading into apo-RBP and retinol release from holo-RBP. This assay played an important role in revealing what STRA6 can do by itself without LRAT or CRBP-I. A. An example of the raw data file for the STRA6-catalzyed retinol loading and retinol release as shown on the Omega Data Analysis software. To initiate the retinol release reaction, holo-RBP is added to STRA6 membrane or control membrane at 0 min. To initiate the retinol loading reaction, retinol is added to STRA6 membrane or control membrane premixed with apo-RBP at 0 min. Fluorescence measurements for 320 nm excitation and 460 nm emission revealed the time course of the reactions. Reactions 1 to 6 monitor retinol loading into apo-RBP (1, 3, and 5 are STRA6 reaction; 2, 4, and 6 are control reactions). Reactions 7 to 12 monitor retinol loading into apo-RBP (7, 9, and 11 are STRA6 reaction; 8, 10, and 12 are control reactions). B. The final calculated signals for reactions shown in A. The left graph was calculated based on reactions 1 to 6. The right graph was calculated based on reactions 7 to 12. The highest fluorescence signal is defined as 1 in the left graph. The fluorescence of holo-RBP added at 0 min is defined as 1 in the right graph.