Figure 2.
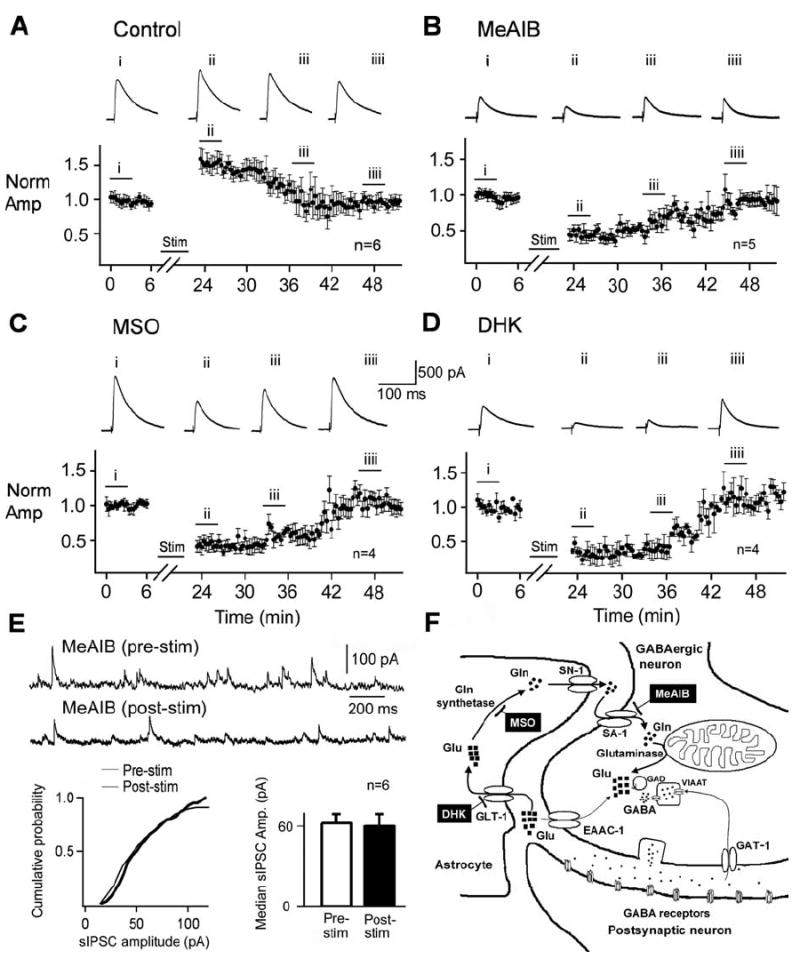
Moderate activity (15 min of 50 Hz, 4 pulse bursts 20 s apart) increased eIPSC amplitude in a glutamate-glutamine cycle-dependent manner. A, eIPSCs are increased after a 15 min period of moderate burst stimulation (stim). Plotted eIPSC amplitude averaged from a group of six recorded cells shows that, after the moderate stimulation, eIPSCs increase over control (A; and traces i and ii; i–iiii are representative traces from one cell averaged over the period indicated). This effect recovers to control levels after 25–30 min (iiii). B–D, Disruption of the glutamate-glutamine cycle reverses this effect, generating a reduction in eIPSCs when moderate stimulation is performed in the presence of the System A transport blocker MeAIB (5 mm;B), the glutamine synthetase inhibitor MSO (1.5 mm; C), or the astrocyte-specific glutamate uptake inhibitor DHK (250 μm; D). Comparing averaged traces (i and ii) from the representative cells in each inhibitor and group data (B–D) show a similar reduction from each blocker after stimulation despite their very different targets (illustrated in F). In all cases, the eIPSC reduction after stimulation recovered within 25–30 min (iiii in B–D). E, A similar reduction in IPSCs poststimulus was not seen in the sIPSCs in the presence of MeAIB, demonstrating that the reduction seen with the eIPSCs was dependent on an increase in synaptic activity. The bar graph in E depicts mean median sIPSC amplitude for six cells before and after burst stimulation. The event numbers in the cumulative frequency distribution are 194 prestimulation and 97 poststimulation. F shows the glutamine cycle through an astrocyte into a GABAergic neuron, starting from glutamate (Glu) uptake into an astrocyte via GLT-1 to glutamine (Gln) synthesis by Gln synthetase and then transport out of the astrocyte and into the GABAergic neuron by the System N (SN-1) and A (SA-1) transporters, respectively. Inside the terminal, Gln is returned to Glu by mitochondrial glutaminases, providing Glu for conversion to GABA by GAD for transport into synaptic vesicles via the vesicular inhibitory amino acid transporter (VIAAT). The various targets for inhibition by MeAIB (B), MSO (C), and DHK (D) are indicated by a bar symbol.
