Figure 3.
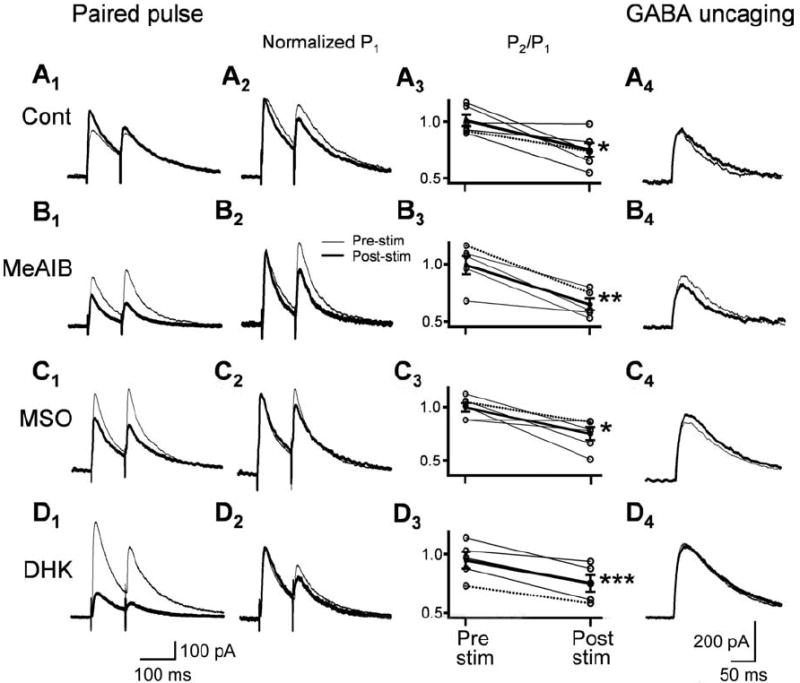
The eIPSC increase after moderate stimulation is attributable to, in part, increased release probability, an effect independent of the poststimulus eIPSC reduction caused by disruption of the glutamate-glutamine cycle. To assess changes in release probability, we performed paired-pulse stimulation before and after the moderate stimulation protocol. Under control conditions in A, the increase in amplitude (representative traces A1; thick line) poststimulus over prestimulus conditions (thin line) is associated with an increase in probability of release. This is revealed when the traces are normalized (A2) to the initial response (P1), showing a relative decrease in the poststimuli response; this indicates increased release probability. This increase in release probability (decrease in P2/P1) was consistent, appearing in every cell tested (A3; thin line and, from representative trace, dotted line) as well as on average (thick line). In the same cell from A1, we elicited fast GABA responses with 1 ms local laser-induced release of CNB-caged GABA (250 μm) before (thin line) and after (thick line) stimulation and found no change in the representative cell (A4), indicating that postsynaptic GABA receptor sensitivity was unchanged by the burst stimulus. Interestingly, this increase in release probability was maintained in the poststim condition when eIPSC amplitude was reduced by glutamate-glutamine cycle inhibitors (B–D). Despite the eIPSC decrease reflected by the poststimulus traces (B1–D1), the normalized representative traces (B2–D2) show a similar P2 reduction in poststimulus conditions as found in control (A2). This maintenance of increased release probability poststimulus is borne out in the group data, showing no difference on moderate stimulation effect on the P2/P1 ratio between control and in the presence of MeAIB, MSO, or DHK (A3–D3). Similarly, from photo-uncaging of GABA, there appeared to be no change in GABA receptor sensitivity from either preburst conditions or compared with control condition in MeAIB (B4), MSO (C4), and DHK (D4). Statistical significance is indicated (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.005).
