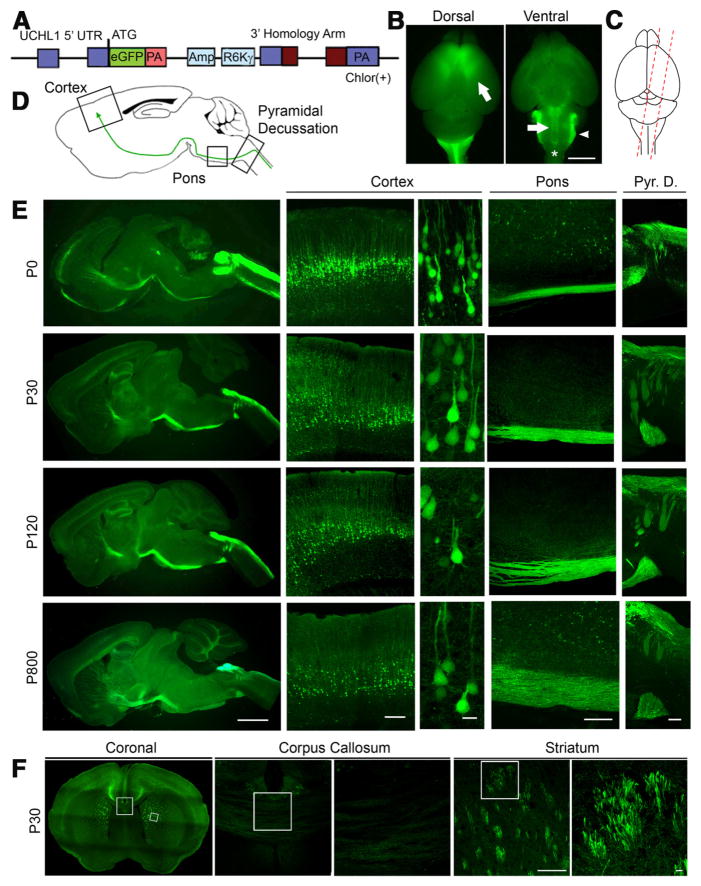
Figure 1.
Cellular and anatomical labeling of large layer 5 pyramidal neurons in UCHL1-eGFP transgenic mice. A, Drawing of BAC construct used to generate UCHL1-eGFP reporter mice. UCHL1 promoter, 5′ UTR; Amp, ampicillin; R6K γ, origin of replication; PA, poly-adenylated tail; eGFP, enhanced green fluorescent protein; Chlor (+), chloramphenicol; UTR, untranslated region. B, Dorsal view shows eGFP expression restricted mainly to prefrontal cortex, including motor cortex (left). Ventral view shows axon bundles of subcerebral projection neurons (SCPN; arrow and star), and brainstem trigeminal ganglion tract (right; arrowhead). C, Sagittal sections are taken with a 15° angle to include motor cortex, pons, and cervical spinal cord in one plane (right). D, Drawing of a sagittal section. Boxed areas represent motor cortex, pons, and pyramidal decussation (Pyr. D.). E, Images of sagittal sections isolated from P0, P30, P120, and P800 brains. D, Confocal images of boxed areas (motor cortex, pons, and Pyr. D.) are enlarged to the right. F, Image of a coronal section at P30. Corpus callosum and striatum are enlarged to the right. eGFP+ axon fibers are detected in the striatum, but not corpus callosum. Images represent intrinsic eGFP expression without immunocytochemical enhancement. Scale bars: B, 3 mm; E (left to right), 2 mm, 250 μm, 20 μm, 200 μm, 200 μm; F, 200 μm, 20 μm.