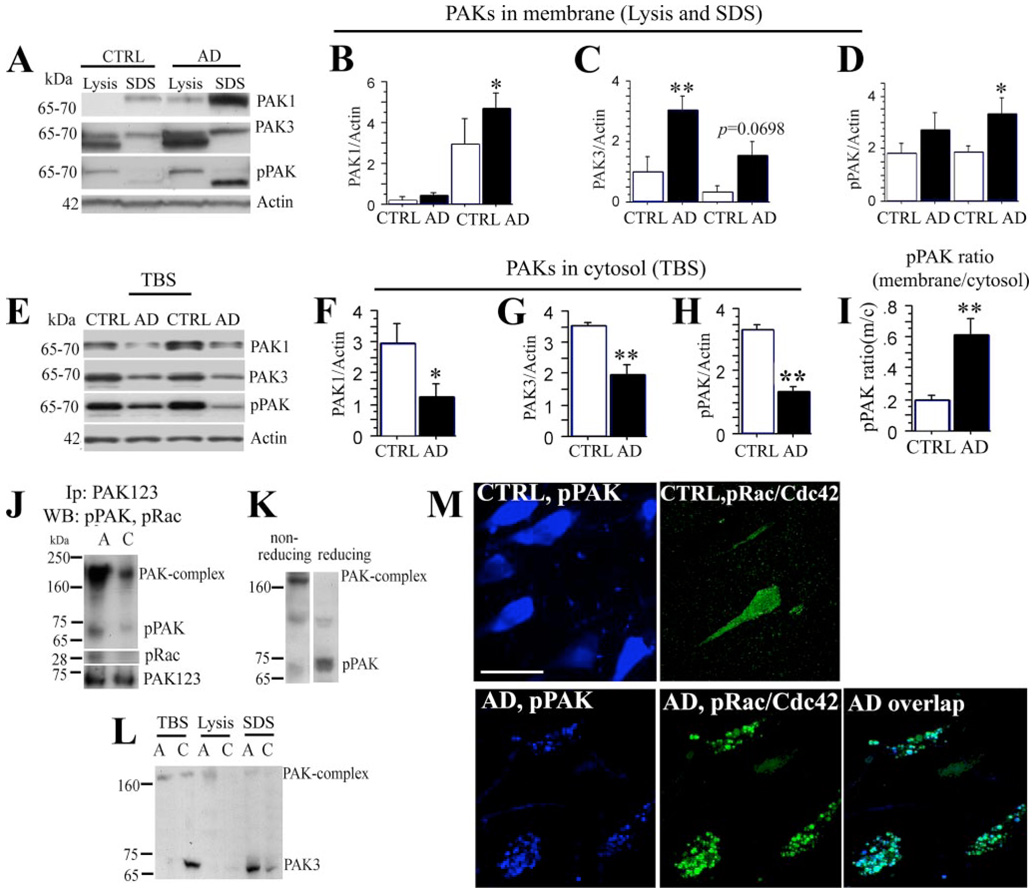
FIGURE 1. PAK/Rac/Cdc42 translocation in Alzheimer disease.
A–H, AD brain tissues from temporal cortex sections were fractionated. The TBS and insoluble-membrano-cytoskeletal (lysis and SDS) fractions separated by SDS-polyacrylamide gel were Western-blotted with anti-PAK1, PAK3, phospho-PAK1–3 (Ser-423) (pPAK) and • -actin antibodies. Lysis and SDS fractions (A) and TBS fractions (E) for PAK1, PAK3, pPAK, and • -actin are shown. CTRL, control. Quantification of immunoblots showed significant changes in • -actin normalized PAK1 (B, *, p • 0.05), PAK3 (C, **, p • 0.01), pPAK in insoluble fractions (D, *, p • 0.05) and in TBS-soluble fractions (F, PAK1, *, p • 0.05; G, PAK3, **, p • 0.01; H, pPAK, **, p • 0.01), and the ratio of pPAK-insoluble versus soluble fractions (I, **, p • 0.01). • -Actin was used for normalization for protein loading. J, immunoprecipitation (IP) analysis of PAK and pRac1/Cdc42 co-translocation in hippocampus in AD. A, AD; C, control. Pooled membrane pellet fractions extracted with lysis buffer from AD or normal human hippocampi were immunoprecipitated with an anti-PAK123 antibody, followed by Western blot detection of pPAK and pRac1/Cdc42. Both levels of pPAK and pRac1/Cdc42 monomer were increased in AD patients as compared with controls. For another strong pPAK immunoreactive band between 160- and 250-kDa size, a potential PAK complex was observed on the same blot and was also increased in AD samples. K, higher molecular weight immunoreactive pPAK present on our standard weakly reducing gels (left) and replaced by lower molecular weight predicted pPAK monomer after boiling with DTT. L, PAK3 translocation in AD brain. PAK3 were elevated in SDS membrane extracts from pooled individual AD cases (n • 5) when compared with normal controls (n • 5), whereas PAK3 in TBS fractions (cytosol) was decreased in the same AD samples. A, AD; C, control. M, active PAK and pRac/Cdc42 were co-translocated in the hippocampus of patients with AD. Anti-pPAK labeled diffuse cytosolic pPAK in normal controls but focal granular structures in AD brain. Anti-pRac labeled weakly in normal controls and when detected labeling was diffuse. Biotinylated pPAK (blue) and phospho-Rac/Cdc42 (green) co-translocation was detected by confocal microscopy in hippocampus from AD brain. Abnormal granular pPAK structures were nearly completely co-localized with pRac/Cdc42 at the membrane of neurons; scale bar, 25 • m.