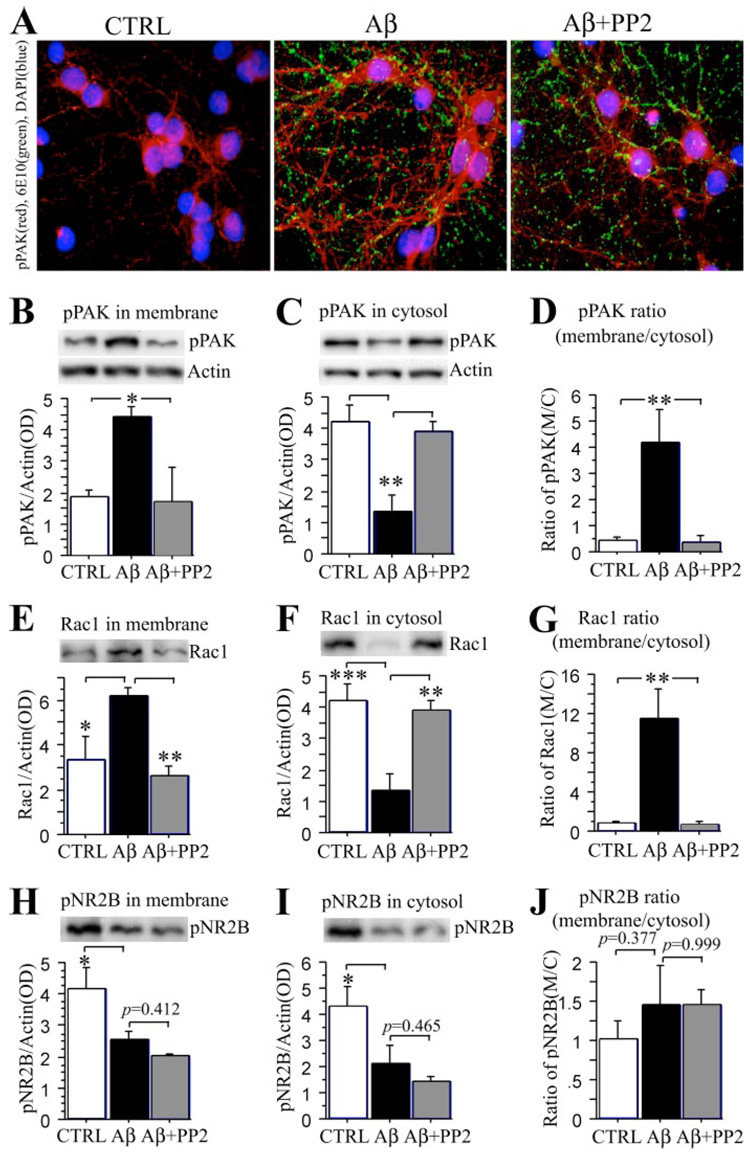
FIGURE 6. Src family tyrosine kinase inhibitor PP2 significantly blocked A• 42-induced PAK/Rac translocation but not NR2B loss in primary neurons.
Hippocampal neurons 10 DIV were treated with 100 nm A• 42 oligomers or A• 42 oligomers plus 10 • m PP2 for 5 h, and pPAK was evaluated by immunofluorescent staining and Western blot. A, immunofluorescent pPAK staining revealed PP2 blocked activation and translocation induced by A• 42 oligomers in primary hippocampal neurons. B–D, PP2 prevents A• 42 oligomer-induced pPAK translocation. pPAK protein levels, measured by Western blot, were significantly increased in membrane and decreased in cytosol fractions by oligomers, whereas PP2 significantly blocked this pPAK translocation when compared with controls (B, *, p • 0.05; C, **, p • 0.01). The ratio of pPAK in the membrane relative to in the cytosol was significantly increased in A• 42 oligomer-treated neurons but not in the presence of PP2 (D, **, p • 0.01). E–G, PP2 prevents A• 2 oligomer-induced Rac1 translocation. Rac1 protein levels, measured by Western blot, were significantly increased in membrane (E, *, p • 0.05) and decreased in cytosol fractions by oligomer treatment (F, ***, p • 0.001), whereas PP2 blocked this Rac1 translocation (E and F, **, p • 0.01) as well as the increased Rac1 membrane/cytosol ratio (G, **, p • 0.01). H–J, Western immunoblot analysis of pNR2B. pNR2B levels were significantly decreased in both membrane and cytosol fractions (H and I, *, p • 0.05); PP2 had no effect on this loss or (p • 0.05) the pNR2B membrane to cytosol ratio (J, p • 0.05). CTRL, control.