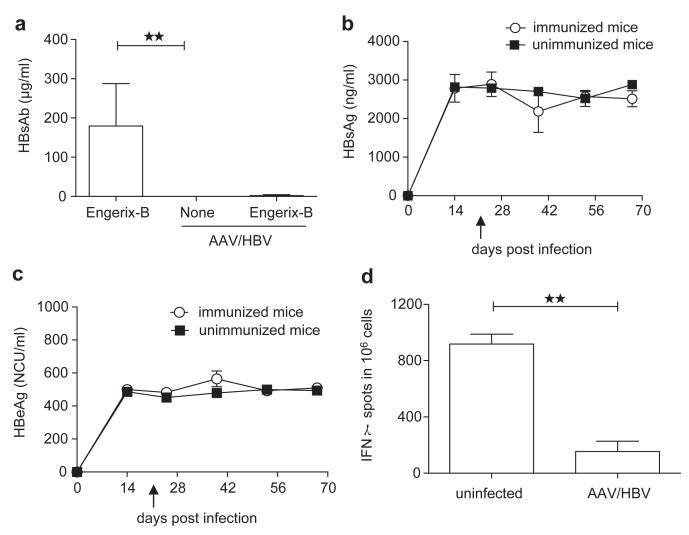
Figure 3.
AAV/HBV infection induces immune tolerance. (a) Adult mice were infected with 1×1011 vg AAV/HBV followed by Engerix-B immunization at 3 weeks post-infection. Serum HBsAb levels were monitored by ELISA at 4 weeks post-vaccination. Uninfected mice immunized with Engerix-B and non-immunized AAV/HBV-infected mice were chosen as controls (n=5). (b) The serum HBsAg titer was monitored by ELISA at different time points pre- and post-Engerix-B immunization (n=3). The arrow indicates vaccine immunization. (c) Following the same immunization protocol, the HBeAg titer was measured by ELISA (n=3). The arrow indicates vaccine immunization. (d) Adult mice infected with AAV/HBV (1×1011 vg) were treated with HBsAg (2 μg/mouse) plus CpG (50 μg per mouse) at 3 weeks post-infection and euthanized on day 10 postvaccination. ENV190-specific CD8 T cells of liver leukocytes were detected by IFN-γ ELISPOT (n=3). AAV, adeno-associated virus; HBeAg, HBV e antigen; HBsAg, HBV surface antigen; HBV, hepatitis B virus.