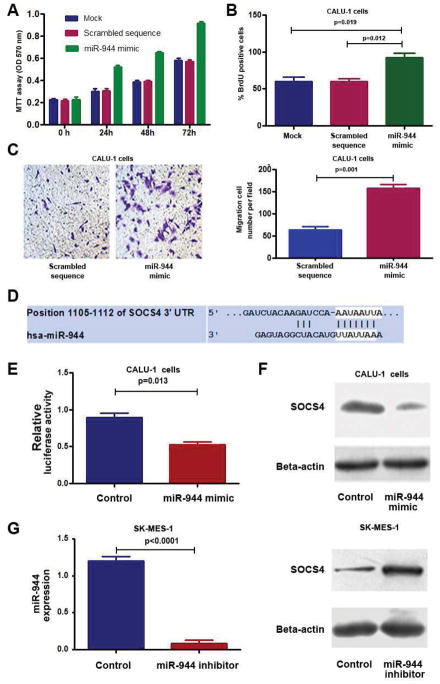
Fig. 3. Dysregulation of miR-944 contributes to tumorigensis of NSCLC by targeting SOCS4.
A, forced expression of miR-944 in CALU-1 cells increased cell growth. B, ectopic expression of miR-944 in CALU-1 cells augmented cell proliferation. C, ectopic expression of miR-944 in CALU-1 promoted cell invasion and migration. The experiments were performed in two cell lines, CALU-1 and H520, and produced similar data. Figures A–C only showed the results from CALU-1 cells. D, a miR-944 target site within 3′-UTR of SOCS4 was predicted by bioinformatic algorithms. E, a luciferase reporter assay in CALU-1 cells showed that luciferase activity of SOCS4-3′UTR was inhibited by increased miR-944 expression. F, Consequently, protein expression of SOCS4 was reduced. G, SK-MES-1 cells that had a high endogenous miR-944 level after transfection with miR-944 inhibitor showed a lower miR-944 level determined by qRT-PCR (left), but a higher SOCS4 level compared with cells treated with control (right). All data were obtained from three independent experiments and shown as mean ± SD.