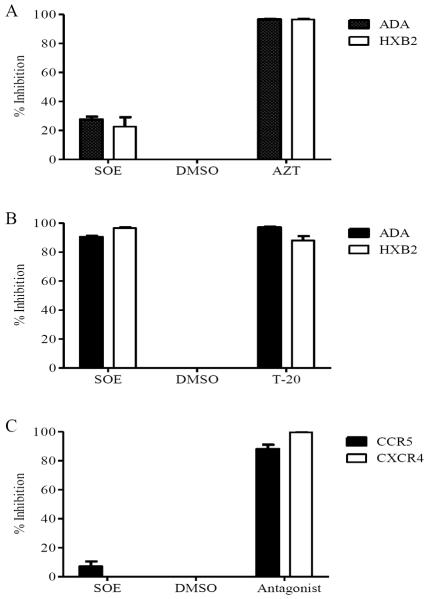
Fig. 2.
SOE inhibits HIV-1 infection by binding to viruses envelope snd block the entry. A. Post-entry assay. GHOST-CD4-CCR5 or CXCR4 cells was co-incubated with pseudovirus for 2 hrs, washed, and then treated with the presence of 50ug/ml SOE, DMSO as negative control and 1uM AZT as positive control for 48 hours. SOE does not inhibit either HIV-1ADA or HIVHXB2 virus gene replication after viral entry is achieved. B. SOE-virus interaction assay. HIV-1ADA and HIVHXB2 pseudovirus pre-treated with 50ug/ml SOE or DMSO as a negative control and entry inhibitor T20 as a positive control. SOE pre-treatment inhibited both HIVADA and HIVHXB2 pseudovirus infection to a similar degree as T-20. C. SOE-cell binding assays. GHOST cells was pre-treatment with SOE or the CCR5 antagonist Marvaroc (MVC) and the CXCR4 antagonist JM2987 as positive controls, and DMSO as negative control for 1 hour at 37°C before being infected with HIV-1ADA or HIV-1HXB2. SOE pre-treatment with the cells had no antiviral effect, while MVC and JM2987 pre-treatment showed strong inhibition against HIV-1 ADA and HXB2 pseudoviruses at 1μM as expected. The data represent the mean ±SD of triplicate experiments.