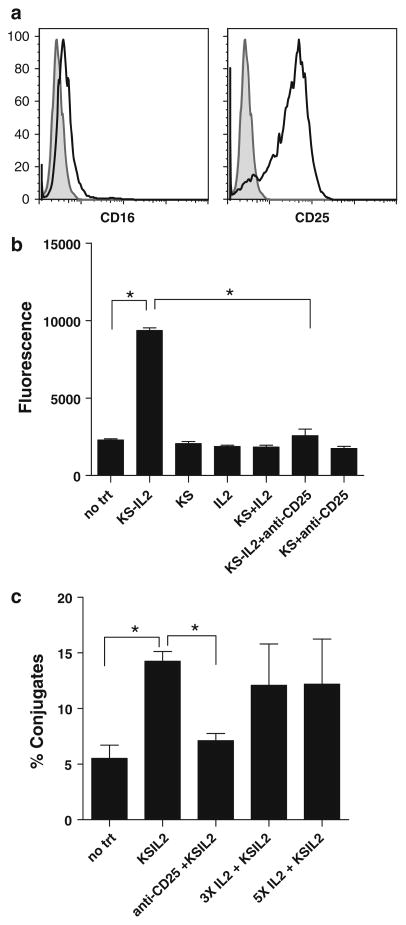
Fig. 4.
NKL cells are a suitable model to study the role of CD25 in IC binding and exhibit increased binding to targets via CD25 in flow cytometry and plate adhesion assays. a CD25 (IL2 receptor alpha chain), and CD16 expression were analyzed by flow cytometry. Shaded area is isotype control. b Fluorescently labeled NKL cells added to confluent, plated OVCAR-3 cells in the presence of the indicated reagents, and then washed off. The residual fluorescence detected is a measure of adherent NKL cells. Increased binding was seen only with huKS-IL2, and this was inhibited with anti-CD25 blocking antibody. c OVCAR-3 and NKL cells were stained with two different cell tracker dyes, and incubated together in the presence of huKS-IL2, anti-CD25 with huKS-IL2, or excess IL2 with huKS-IL2. Cell conjugates were measured using flow cytometry. *P <0.05