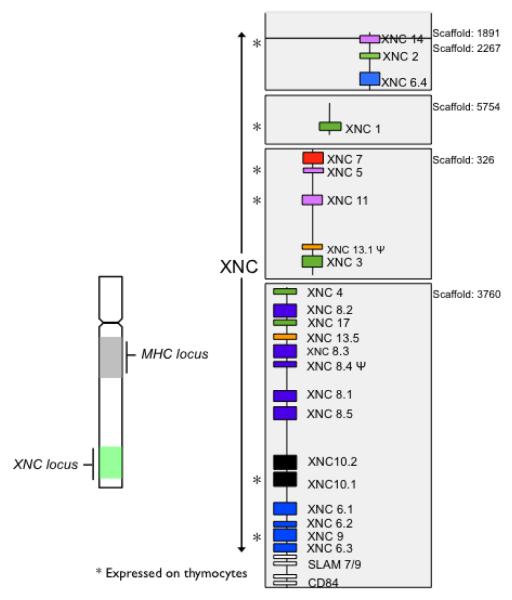
Figure 1. Genomic organization of X. laevis nonclassical MHC class I genes.
XNCs are located distally from the MHC locus on the same chromosome with the MHC in the middle of the long arm and the XNC locus at the tip of the same arm [84]. Organization of the 23 XNC genes including pseudogenes, indicated by Φ. XNC genes are located on five different scaffolds based on the Xenopus laevis Genome project http://xenopus.lab.nig.ac.jp, XenVis 2.0 assembly. The number of each scaffold is indicated on the right. XNC genes expressed on tadpole thymocytes are indicated by a *. Orthologous relationships defined by multiple sequence alignments and neighbor-joining phylogenetic analysis of the α1/α2 domains of XNC genes are indicated by colors with each color representing a phylogenetic grouping based on a bootstrap value of >95. Flanking unrelated genes are shown as white boxes.