Figure 1. Acute MGO treatment led to activation of Kir6.1/SUR2B channel.
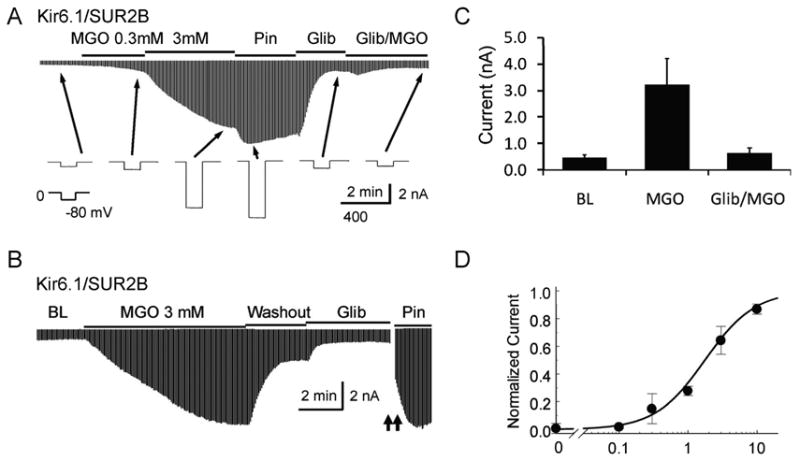
A, Kir6.1/SUR2B channel was expressed in HEK293 cells. Whole-cell currents were recorded from cells two days after transfection in voltage-clamp configuration. MGO (0.3 mM – 3 mM) led to the activation of Kir6.1/SUR2B currents in a concentration-dependent manner. Pinacidil (Pin, 10 μM), a KATP channel specific opener, could further open the channel. The application of KATP channel specific inhibitor glibenclamide (Glib, 10 μM) dramatically reduced the current. In the presence of Glib (10 μM), the effect of higher concentration of MGO (10 mM) on channel activation was completely blocked. B, The MGO-mediated channel activation was reversible. Following channel activation, MGO washout with the bath solution returned the KATP channel currents to almost baseline level. Glib caused a further decrease in the KATP channel currents. C, Summary of the effect of MGO on the KATP channel currents in the presence and absence of Glib. D, Dose-response relationship between the concentration of MGO and the normalized current. Data was described by the Hill-equation with EC50 of 1.7 mM.
