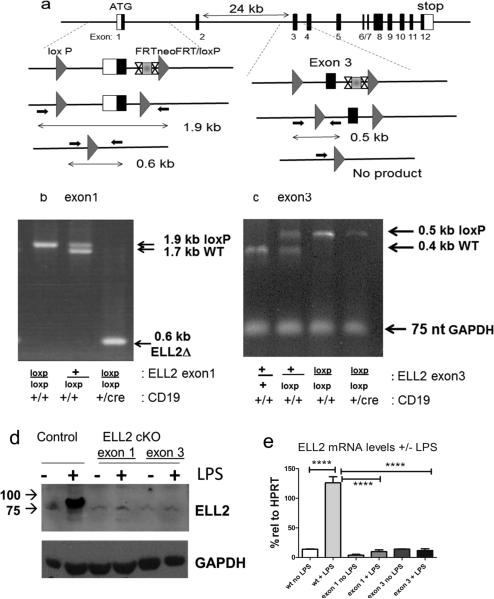
Figure 1.
ELL2 loxp/loxp mice have efficient deletion of ELL2 in B cells
a. Strategy for generating alleles of ELL2 with either exon 1 or exon 3 flanked by loxp sites (triangles). The FRTneo gene flanked by sites indicated as X...X is deleted in ES cells in both models. Loxp sites are indicated by the grey triangles. The small arrows indicate the primers used to generate PCR fragments of 1.9 kb (plus 2 loxP sites) and 1.7 kb (no loxP) for exon 1. Deletion between the two loxP sites in the presence of CR19cre/+ generates a 0.6 kb PCR fragment. The small arrows in exon 3 flank one of the loxP sites to generate PCR fragments of 0.5 kb (plus loxP) and 0.4 kb (no loxP). Absence of a 0.5 kb product indicates deletion between the two loxP sites with CD19cre/+ .
b. PCR analysis to detect the 0.6 kb deletion product in the presence of CD19cre/+ in B cells.
c. PCR analysis showing deletion of the 0.5 kb fragment in the presence of CD19cre/ +. The GAPDH DNA PCR product indicates that there is the same amount of DNA in each sample.
d. Immunoblot of nuclear lysates from splenocytes +/− 20 ug/ml LPS for 4 days of ELL2 loxp/loxp mice with CD19 cre/+ or CD19+/+. Proteins were run on a denaturing polyacrylamide gel, blotted and probed with affinity purified rabbit anti-ELL2 peptide (R4502) as previously described.
e. mRNA levels of ELL2 with or without LPS stimulation four days after addition in control and ELL2loxp/loxp CD19 cre/+ mice was quantified relative to HPRT control RNA, set as 100% by real-time, quantitative PCR. N>5 each group. P=0.001 (***). Error bars indicate SEM, here and throughout.