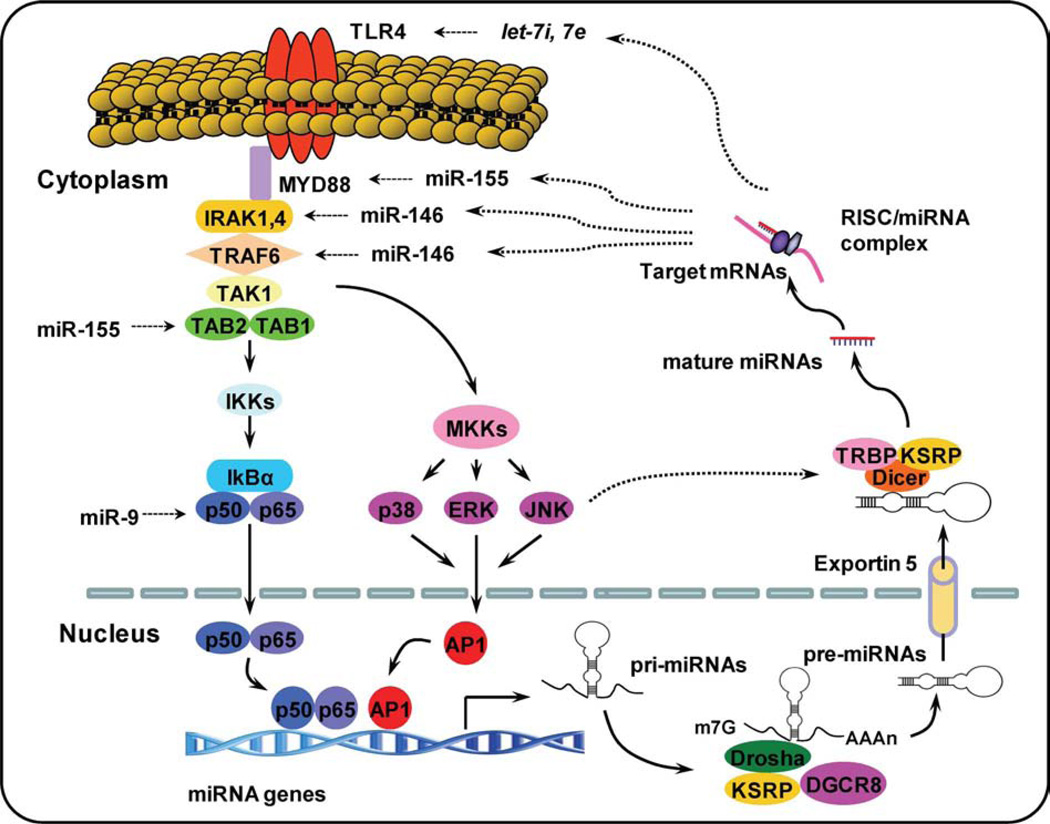
Figure 1.
Intricate network of TLR signaling and miRNAs. Upon specific microbial recognition, TLR recruit adaptor proteins and activate downstream signaling cascades that activate NF-κB signaling pathway and MAPK signaling pathway. This activation induces the expression of inflammatory mediators and miRNA genes. After stimulation, pri-miRNAs are transcribed by RNA polymerase II and cropped into pre-miRNAs. Pre-miRNAs are actively transported to the cytoplasm byexportin-5 where they are cleaved by the enzyme, Dicer, to form mature miRNAs. miRNAs have been shown to regulate multistep of TLR signaling indicated by dotted line. AP-1, activator protein-1; IKK, IkappaB kinase; IRAK, IL-1 receptor-associated kinase 1; KSRP, KH-type splicing regulatory protein; miRNAs, microRNAs; MKK, mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) kinase; MyD88, myeloid differentiation primary response gene 88; RISC, RNA-induced silencing complex; TAB1, transforming growth factor activated kinase-1-binding protein 1; TAK1, transforming growth factor activated kinase-1; TLR, Toll-like receptor; TRAF, TNF receptor-associated factor; TRBP, TAR RNA-binding protein.