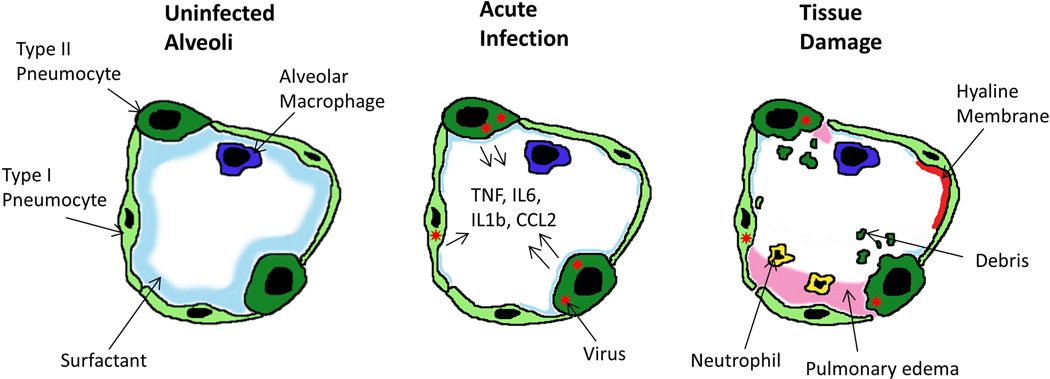
Figure 2.
Model of an infected alveolus in the lung. Type I and type II pneumocytes make up the alveolar walls, resident alveolar macrophages and pulmonary surfactant exist in the airspace (A). In the acute phase of SARS-CoV infection (B) type I and type II pneumocytes are infected and secrete inflammatory cytokines while surfactant levels decrease. During the late stage/tissue damage portion of viral infection viral titres decrease while airway debris, pulmonary oedema and hyaline membrane formation all impede respiration (C).