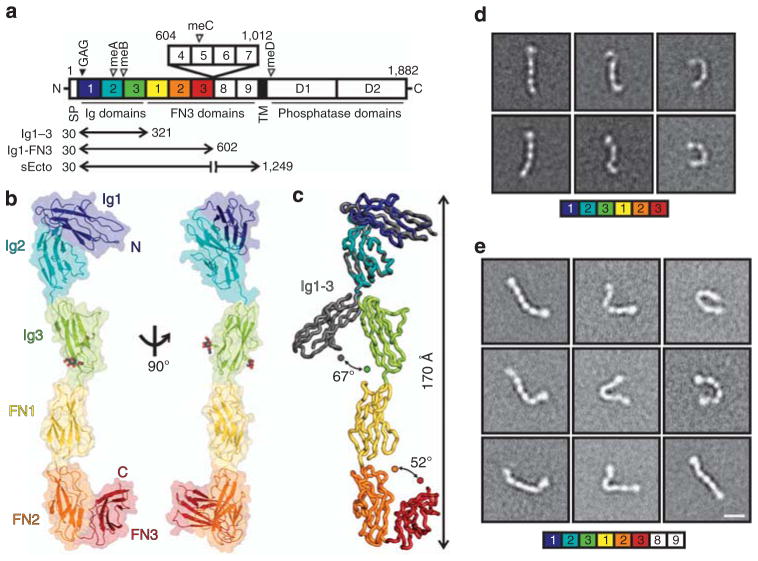
Figure 1. RPTPσ ectodomain flexibility.
(a) RPTPσ domain organization. N, amino-terminus (extracellular); SP, secretion signal peptide; TM, transmembrane; C, C terminus (intracellular); Ig, immunoglobulin-like; FN, fibronectin type-III; GAG, glycosaminoglycan-binding site (filled arrowhead). Alternative splicing inserts: FN domains 4–7 and mini-exons A–D (open arrowhead). (b) Ribbon and surface representations of the human RPTPσ Ig1-FN3 crystal structure. N-linked glycans in atom representation. (c) Ig3 movement in Ig1-FN3 relative to Ig1–3 (grey, PDB ID: 2YD9) structure. Representative RPTPσ Ig1-FN3 (d) and RPTPσ sEcto (e) negative-stain electron microscopy class averages. Scale bar, 10 nm. Full sets of RPTPσ Ig1-FN3 and sEcto class averages are provided in Supplementary Figs 2 and 3.