Figure 4. Universal electrophoretic mobility shift assay (uEMSA) validation of Rv0494 binding. A).
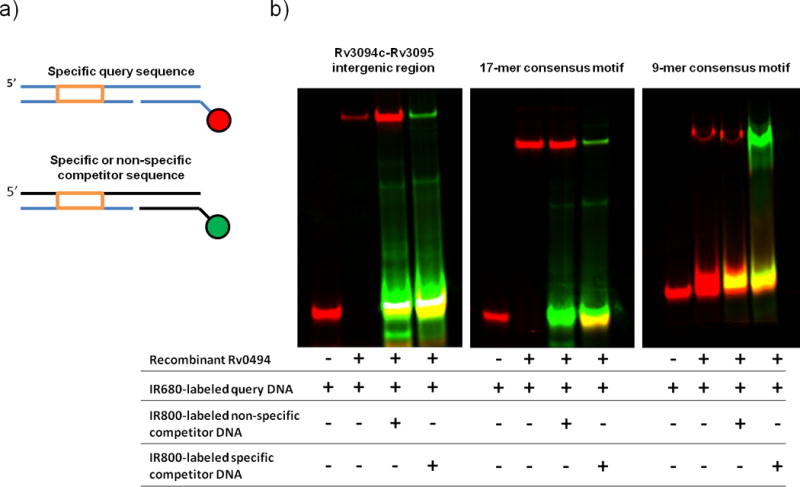
Schematic of DNAs used in uEMSA experiments. Three DNAs are annealed to form a single dsDNA product: a specific query sequence (orange box) is annealed in a 3-piece dsDNA fragment to a unique 12-mer sequence covalently coupled to a reporter dye. In these experiments, the specific query DNA was labeled with IR680 (red) and specific or non-specific competitor DNAs were labeled with IR800 (green). B) Purified recombinant Rv0494 binds specifically to ChIP-identified wildtype sequence (left panel), the 17-mer consensus motif (middle panel), and the 9-mer consensus motif (right panel). In the absence of protein, dye-coupled DNA does not shift (lane 1); however, the protein-DNA complex runs at a higher molecular weight (lane 2). This protein-DNA complex persists in the face of 20x molar excess green-labeled non-specific competitor DNA (lane 3), but can be outcompeted by the addition of 20x molar excess green-labeled specific competitor DNA (lane 4).
