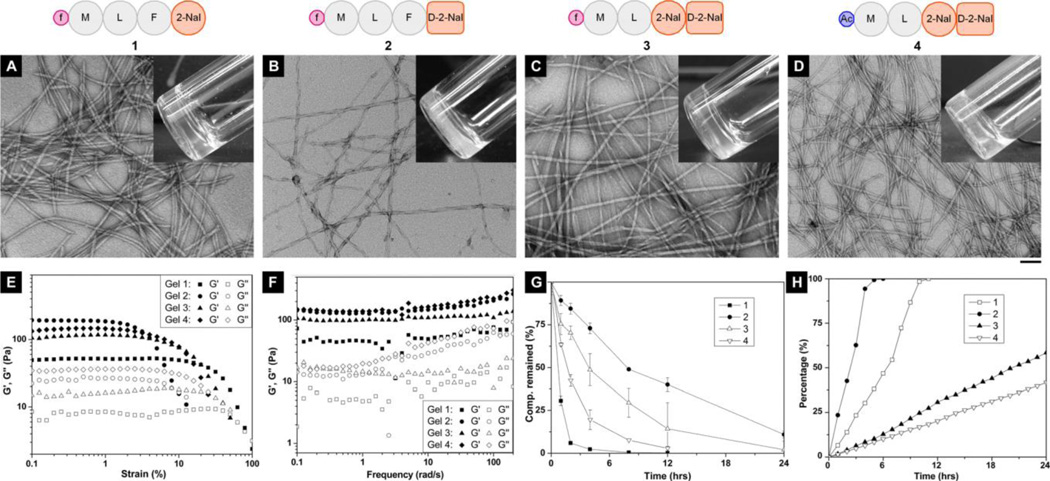
Figure 1. Characterization of fMLF-derived hydrogelators (1, 2, 3) and a control peptide (4) and the hydrogels.
(A-D) The typical TEM images of negatively-stained fibrils of (A) the hydrogels of 1 (0.20 w/v%), (B) 2 (0.40 w/v%), (C) 3 (0.125 w/v%), and (D) 4 (0.075 w/v%), respectively, with the molecular representation on top (all hydrogels are at pH = 7.4 in DPBS buffer; the scale bar is 100 nm; denotation: Ac = acetyl; inset: the optical images of the hydrogels ). (E) Strain sweep and (F) frequency sweep of the hydrogels with the same concentrations as the hydrogels prepared for optical images and TEM. (G) The digestions of 1, 2 and 3, respectively, in 3.5 mL HEPES buffer solution of 1.4 mg (0.4 mg/mL) by adding 2.8 µL of proteinase K solution at 37°C. (H) The release profiles of the monomers from the hydrogels of 1, 2, 3 and 4 (0.4 w/v%) at 37°C.