Fig. 6.
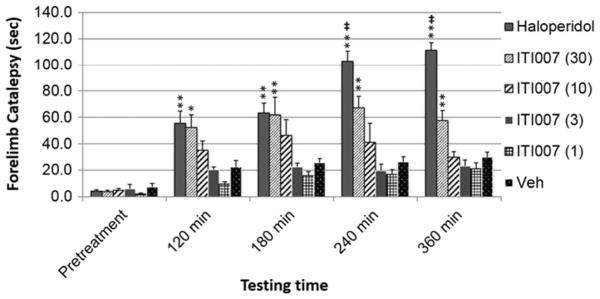
Effect of haloperidol and ITI-007 on motor performance as measured by forelimb catalepsy. Forelimb catalepsy was measured in mice using the bar grip test. Animals received a single oral dose of vehicle (Veh) (0.5 % methylcellulose in water, 6.7 ml/kg volume, p.o.) or haloperidol (3 mg/kg) or ITI-007 (1–30 mg/kg) in vehicle solution. Catalepsy was then measured in mice (N=4/dose/drug) by recording the latency (in seconds) to step both front paws down to the floor of the cage up to a maximum time of 120 s. Catalepsy scores were recorded for each mouse at 120, 180, 240, and 360 min after drug administration. Mean forelimb catalepsy time (in seconds) was calculated across each group and time point. Data were analyzed using ANOVA with Newman–Keuls post hoc test. Data are presented as mean±SEM. *p<0.05; **p<0.01 compared with vehicle treatment. ‡p<0.01, statistically significant difference between haloperidol and ITI-007 treatments
