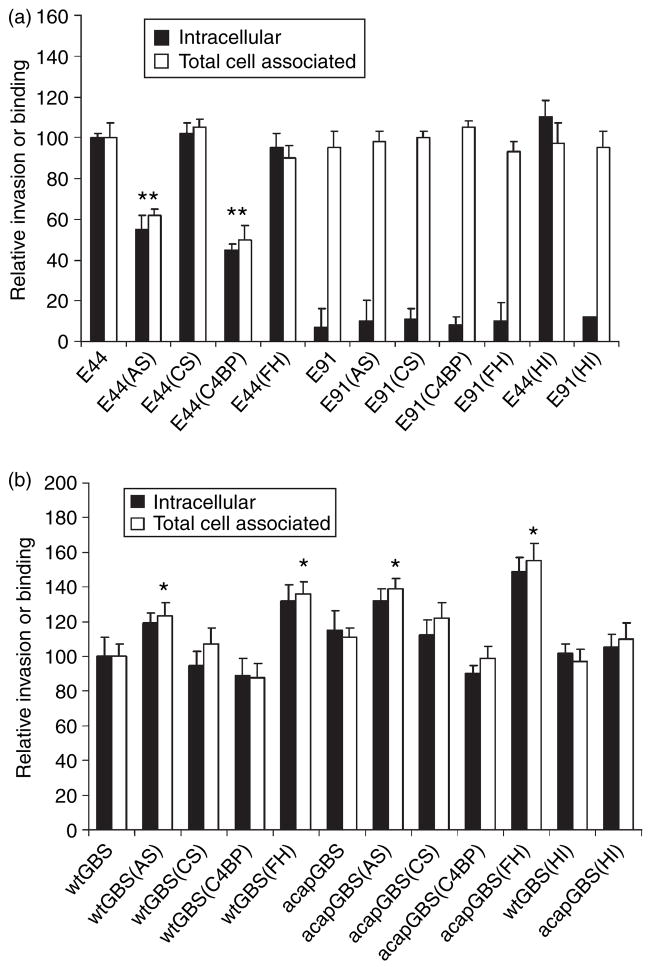
Figure 5.
Binding to and invasion of human brain microvascular endothelial cells (HBMEC) by Escherichia coli and group B streptococci (GBS) incubated in adult serum (AS), cord serum (CS), puri- fied Factor H (FH), or C4-binding protein (C4BP). (a) OmpA+ E. coli (E44) or OmpA− E. coli (E91) and (b) wild-type GBS (wt-GBS) or acapsular GBS (acap-GBS) were incubated in 40% cord serum (CS) or adult serum (AS), purified Factor H (FH) or C4-binding protein (C4bp) (25 μg/ml) for 15 min, washed, and added to HBMEC monolayers at a multiplicity of infection of 1 : 100 (cell to bacteria ratio). Binding and invasion assays were performed as described in the Materials and methods. Heat-inactivated (HI) serum was used as a negative control. The experiments were repeated three times in triplicate with similar results. The data are presented as means ± SD. The invasion of the bacteria treated with serum was considered signifi- cantly enhanced or reduced when compared to untreated controls. *P < 0.02 by two-tailed t-test; **P < 0.05.