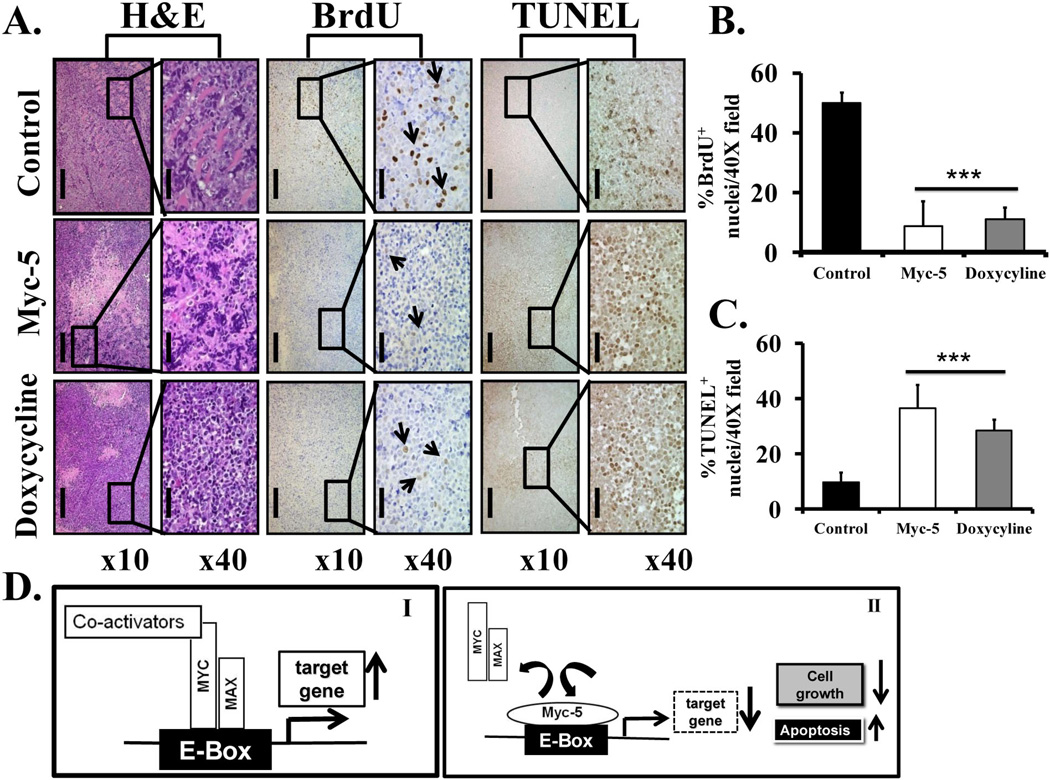
Figure 6. Histopathology of xenografts in nude mice and illustration of potential mechanism by Myc-5.
A, Tissue sample were analyzed qualitatively for the morphological changes. Magnification of all pictures is ×10 (scale bar 200µm) and ×40 magnification (scale bar 50µm). B–C, Quantitative data of immunohistochemical analysis of BrdU and TUNEL positive staining in each group. The data in B and C are shown as the mean ± SD of three tumor samples from an individual mouse in each group.. Statistical significance was calculated by Student's t test. ***P < 0.001. D, Schematic diagram of the mechanism by which PI polyamide inhibits MYC/MAX interaction to E Box. (I), MYC/MAX dimer binds to E-box and activates MYC target gene expression. (II), Myc-5 occupied the E-box by binding, thereby inhibiting the MYC/MAX interaction to E-box further causing suppression of target gene expression.