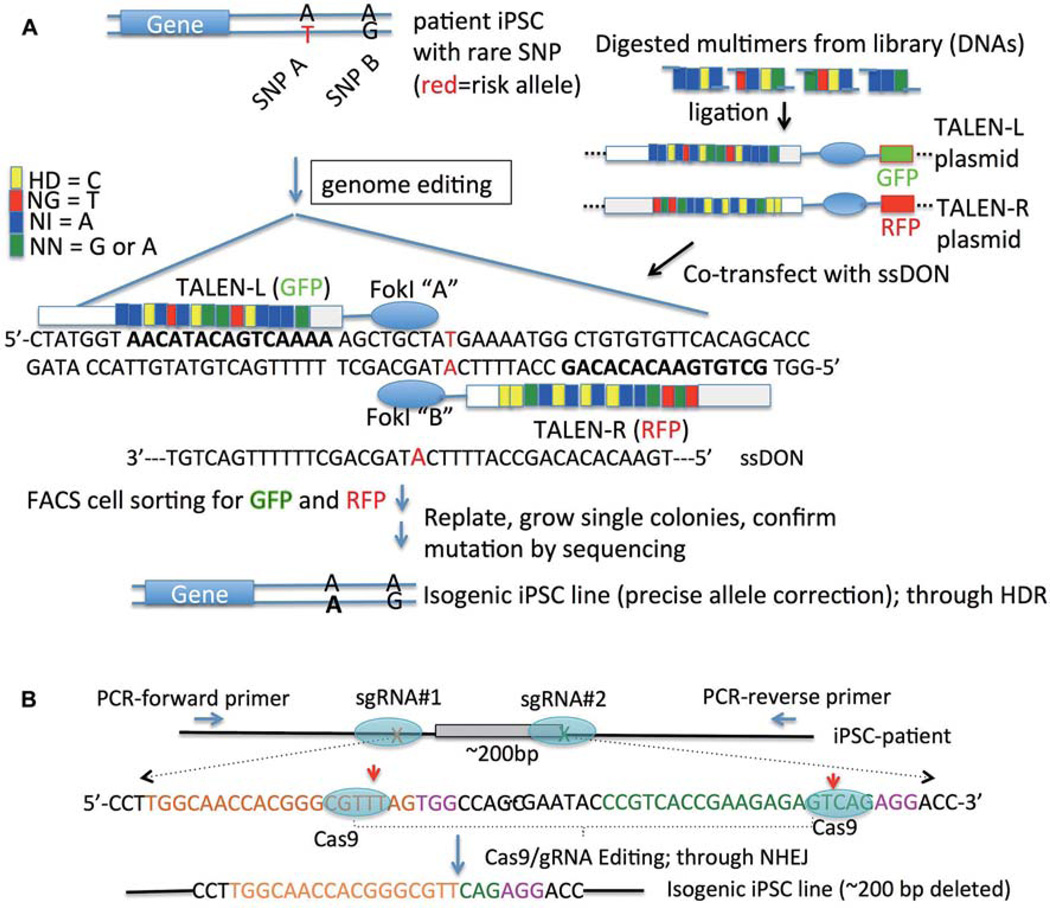
Fig. 3.
Genome editing to create isogenic patient-specific iPSCs. (A) TALEN plasmids are used for precise risk allele correction (T to A for SNP A) through ssDON (single-stranded DNA oligonucleotide)-mediated homology-directed repair. (B) CRISPR/cas9-mediated an exon deletion (~200 bp) using paired sgRNAs (#1 and #2) for targeting. An isogenic iPSC line is generated with ~200 bp DNA being deleted through non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ) of the double-strand breaks of DNA. In each sgRNA, the specific target sequence (20 nt, green or orange) must immediately precede a 5′-NGG adjacent motif (PAM; pink). The red arrow indicates the expected cut site (~3 bp upstream of the NGG PAM sequence) of Cas9 nuclease. Flanking PCR primers can be designed for a rapid screen of iPSC clones carrying the deletion allele.