Figure 1.
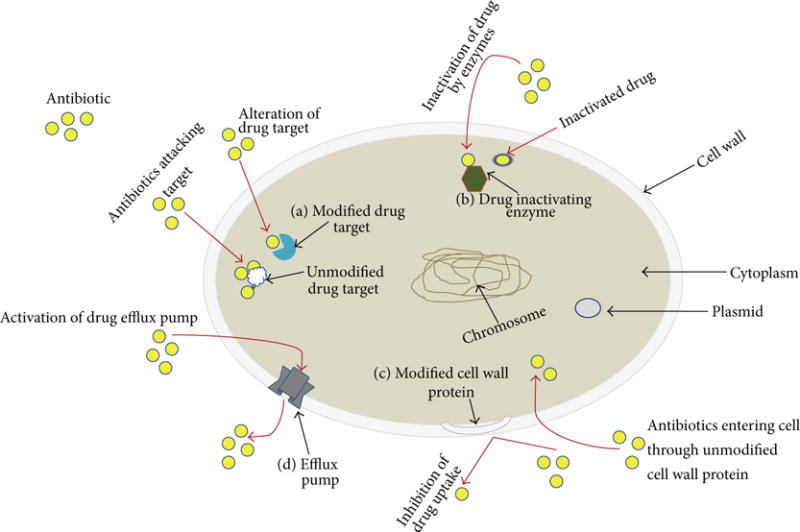
Mechanisms representing antibacterial resistance. A generic bacterium is depicted in which various mechanisms for resistance to antimicrobial agents are indicated. (a) Drug target modification, (b) drug inactivation by enzymes, (c) reduced drug permeability by membrane modification, and (d) active efflux of drugs from the bacterial cell. Yellow circles indicate antimicrobial agent molecules; red arrows indicate movement of molecules, and black arrows are pointing to intra- and extracellular structures.
