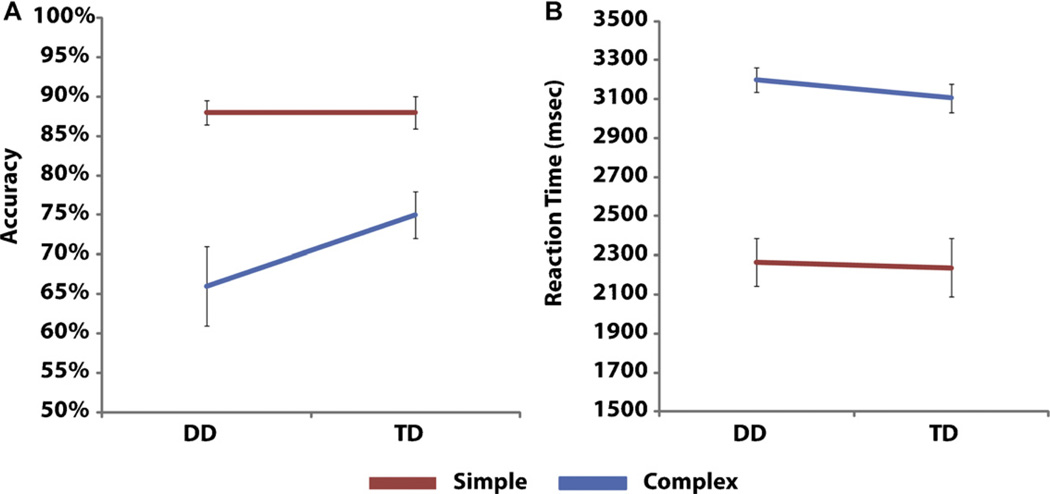
Fig. 1.
(A and B) Behavioral performance in the DD and TD groups. Both groups showed strong differences between addition problem type, with Simple problems being performed faster and more accurately than Complex problems. There were no group differences in either accuracy or RT. However, the interaction between problem type and group was marginally significant (p = .06) indicating weaker performacne for Complex problems in the DD group.