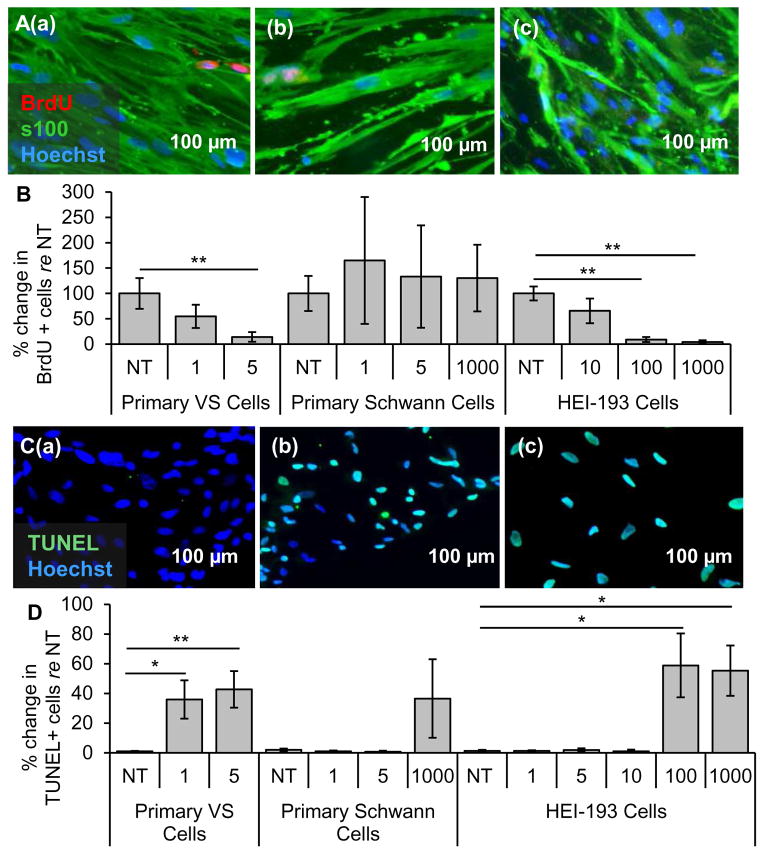
Figure 5.
Clinically-relevant NF-κB inhibitor curcumin leads to selective decrease in proliferation and survival of VS cells. A. Representative proliferation images for primary VS cultures treated with (a) no treatment (NT), (b) 5, (c) 20, and (d) 50 μM curcumin. BrdU in nuclei (red) marks proliferating cells. B. Quantification of proliferation changes after treatment with curcumin at 5, 20, and 50 μM in primary VS cells, primary Schwann cells and HEI-193 NF22 VS cell line, all normalized to proliferation in control NT cells (n≥3); C. Representative cell death images are shown for primary VS cultures treated with (a) NT, (b) 5, (c) 20, and (d) 50 μM curcumin. TUNEL (green) marks dying cells. D. Quantification of cell death rate after treatment with curcumin at 5, 20, and 50 μM in primary VS cells, primary Schwann cells and HEI-193 NF2 VS cell line (n≥3). *p<0.05, **p<0.01, re = compared to. Error bars represent SEM. Nuclei are labeled with Hoechst (blue) in (A, C).