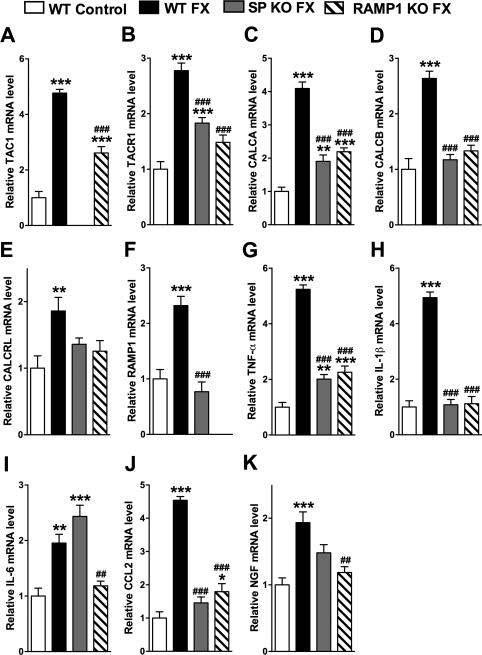
Figure 6. Substance P deficient (SP KO) and CGRP RAMP1 receptor deficient (RAMP1 KO) fracture (FX) mice failed to develop exaggerated spinal neuropeptide signaling and inflammatory mediator expression at 3 weeks post-fracture, measured by real-time PCR.
Similar to the changes observed in 4 weeks post-fracture rats (Figs. 1,3), in wild type (WT) fracture (FX) mice there was increased gene expression of (A) SP (TAC1), (B) SP NK1 receptor (TACR1), (C, D) CGRP (CALCA and CALCB), (E) CGRP CRLR receptor (CALCRL), (F) CGRP RAMP1 receptor (RAMP1), (G) TNF-α, (H) IL-1β, (I) IL-6, (J) CCL2, and (K) NGF, compared to WT mice with no fracture (WT Control). Substance P deficient fracture (SP KO FX) mice had attenuated post-fracture spinal cord changes compared to WT FX mice, and there was no increase in the expression of (D) CALCB, (E) CALCRL, (F) RAMP1, (H) IL1β, and (K) CCL2 in the SP KO FX mice, compared to WT control mice. CGRP RAMP1 receptor deficient fracture (RAMP1 KO FX) mice also exhibited attenuated post-fracture spinal cord changes, compared to WT FX mice, and there was no increase in (B) TACR1, (D) CALCB, (E) CALCRL, (H) IL-1β, (I) IL-6, and (J) NGF mRNA levels, compared to WT controls. (A) TAC1 mRNA was not detected in the TAC1 deficient mice and (F) RAMP1 mRNA was not measurable in the RAMP1 receptor deficient mice. Values are means ± SE, n=8 per cohort. One-way ANOVA (p < 0.01 for graph E, p < 0.001 for all other graphs), with Bonferroni post hoc testing *P< 0.05, ** P< 0.01 and *** P< 0.001 for WT FX, SP KO FX, or RAMP1 KO FX vs WT Control, # p< 0.05, ## p< 0.01 and ### p< 0.001 for SP KO FX, or RAMP1 KO FX vs WT FX.