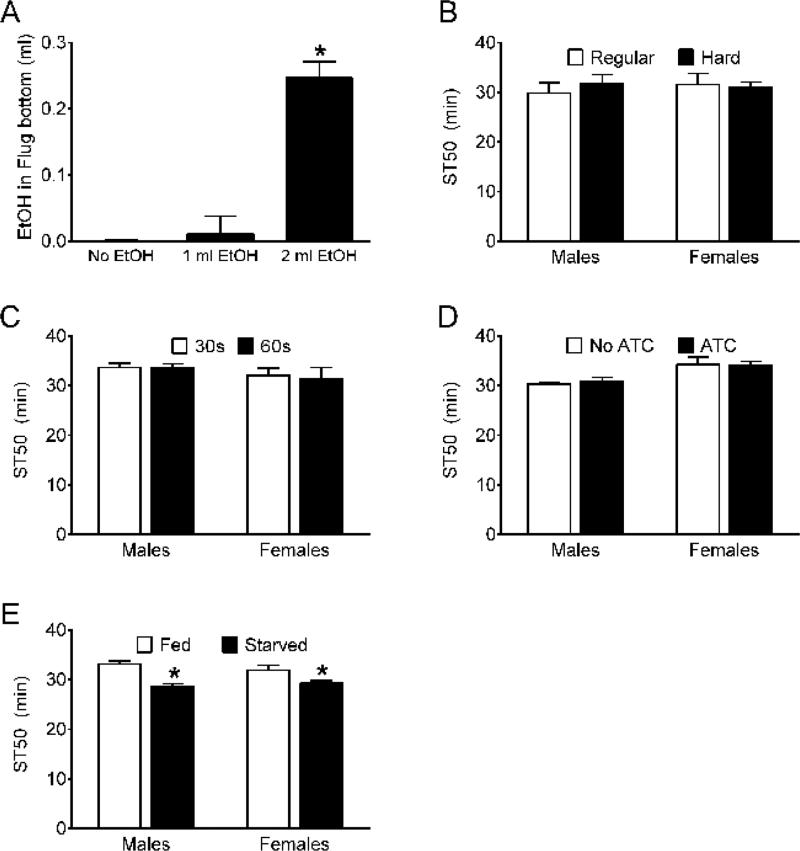
Figure 2. Assessment of operational parameters in the sedation assay.
(A) Amount of ethanol in the bottom 2 mm of cellulose acetate plugs. The volume of ethanol added to the tops of cellulose acetate plugs had a significant effect on the volume of ethanol that moved into the bottom 2 mm of cellulose acetate plugs during a mock 60 min experiment (one-way ANOVA, p <0.0001; *Bonferroni multiple comparison test, 2 ml vs 0 and 1 ml, p <0.05 n = 4). Ethanol was quantitated as a change in mass of the cellulose acetate plugs. (B) Neither vigor of tapping the vials during testing (Regular, Hard) nor sex of the flies tested affected ST50s (two-way ANOVA; effect of tapping, n.s.; effect of sex, n.s.; n = 12). (C) Neither recovery time after tapping nor sex had significant effects on ST50s (two-way ANOVA; effect of recovery time, n.s.; effect of sex, n.s.; n = 6). (D) Inclusion of antibiotics (ATC; ampicillin, tetracycline and chloramphenicol) in the growth medium had no overall effect on ST50s, but there was an effect of sex on ST50 (two-way ANOVA; effect of ATC, n.s.; effect of sex, p = 0.001; interaction, n.s.; n = 6). (E) Effect of starvation on ethanol sedation sensitivity. ST50s were significantly lower in flies deprived of food and water for 6 hr (Starved) compared to normally fed (Fed) flies; ST50s in males and females were indistinguishable overall (two-way ANOVA; effect of starvation, p <0.0001; effect of sex, n.s.; n = 12; *Bonferroni multiple comparison tests, effect of starvation in males and females, p <0.05).