Figure 4.
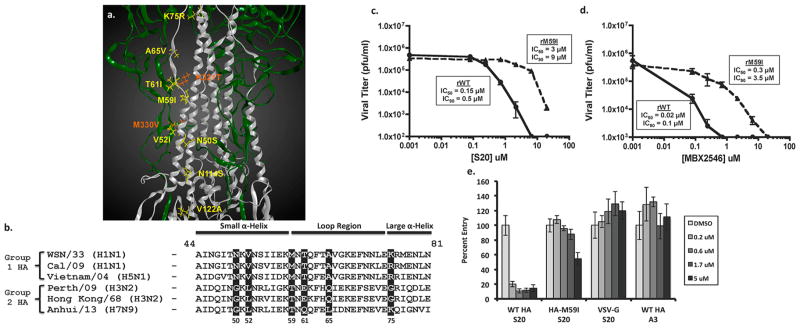
Mutations within the HA protein cause resistance to the inhibitory effects of S20. (a) Crystal structure of A/PR/8/34 HA (PDB 1RU7) protein showing the HA1 (green) and HA2 (silver) subunits. Residue positions where S20 escape mutations occurred are indicated in orange (HA1) and yellow (HA2). (b) Sequence alignment of group 1 and 2 HA proteins within the region of highest escape mutation density. Positions of escape mutations are shaded. WSN amino acid numbering is used in both panels a and b. Virus titers from A549 cells infected with either rWSN-WT or rWSN-HA/M59I viruses (MOI = 0.01) were treated with increasing concentrations of (c) S20 or (d) MBX2546 for 24 h. Curves represent means of triplicate values ± SD. IC50 and IC90 values are indicated. (e) S20 inhibition of VSV-G, WSN HA/NA, or WSN HA-M59I/NA containing pseudotyped particles in A549 cells. The non-entry inhibitor A3 was used as a negative control. The samples were tested in triplicate, and the data are presented as the mean ± SD.
