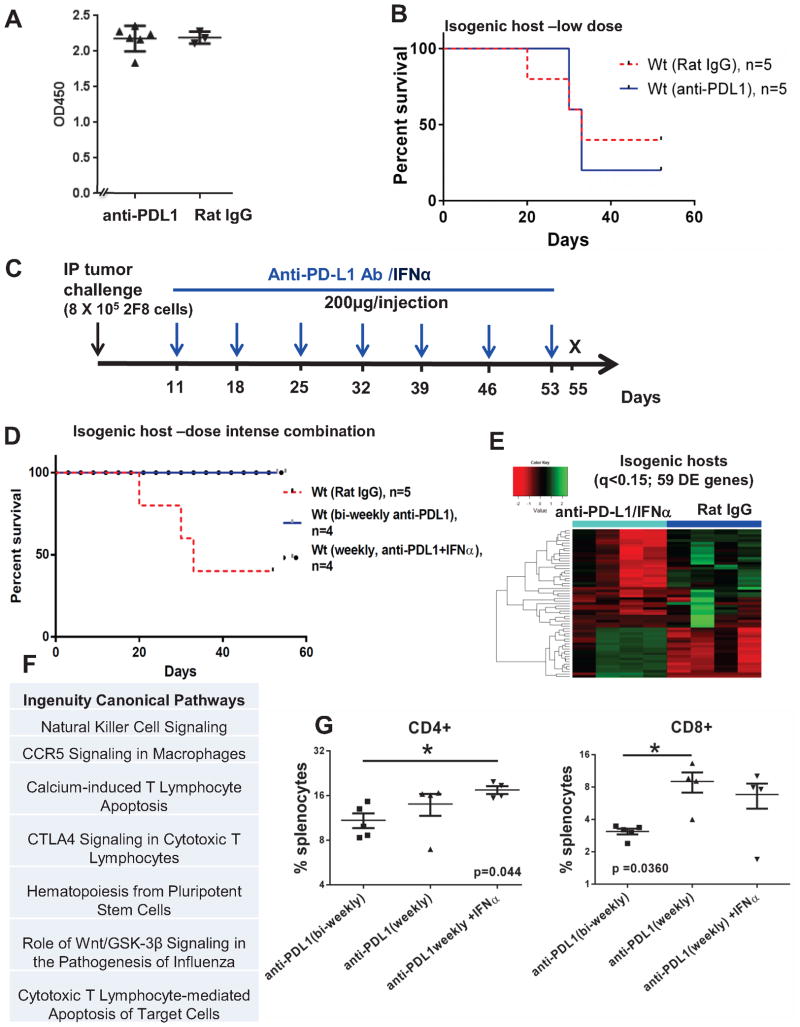
Fig. 4.
Weekly anti-PD-L1 intraperitoneal injections started early increase survival in WT mice with high levels of naturally occurring anti-tumor antibodies. A ELISA measurement of anti-MUC1 IgG antibodies in sera from non-MUC1 transgenic littermates (WT mice) challenged IP with 8x105 2F8 cells. The optical density (OD) at 450 nm is shown on the y axis. B Kaplan Meyer survival curve of survival in wild type mice treated bi-weekly with isotype control (n=5, dotted line) or anti-PD-L1 antibody (n=5, solid line). C Modified protocol schema for dose-intense weekly treatment, starting at day 11 post-tumor challenge. Mice received weekly anti-PD-L1 alone or in combination with IFNα (10000 IU). D Kaplan Meyer curve of survival for WT mice treated with IgG (n=5, red intermittent line), anti-PD-L1 (black circles) or anti-PD-L1/IFNα (n=4, blue solid line). E Heat map analysis of 59 DE genes by Nanostring (q <0.15) of which 20 were upregulated and 39 were downregulated in anti-PD-L1/IFNα treated (n=4) versus control animals (n=4). F Top 7 canonical pathways identified through IPA, using the 59 genes in panel E. G Percentages of splenic CD3+ T cells by flow cytometry. **, p<0.001, ANOVA.