Fig. 4. RTR attenuates LPS-induced pulmonary microvascular permeability.
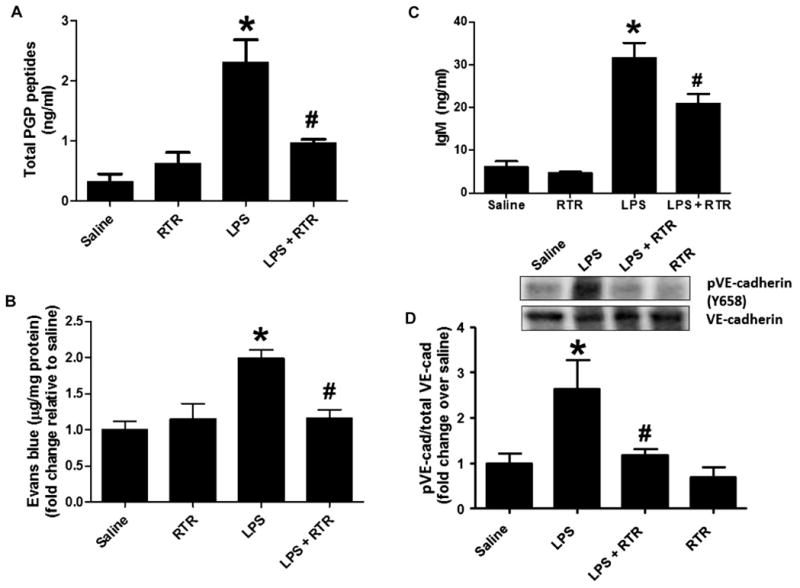
Mice were injected via the tail vein with 50 μl of PBS alone or containing 50 μg of RTR and then intraperitoneally administered with 75 μg of LPS (in 100 μl of PBS) once a day. (A) After 4 days of treatment, mice were sacrificed for serum measurements of PGP (n = 6) or injected via the tail vein with Evans blue. (B) Evans blue leak to the lung was quantified and normalized to protein; data show fold change relative to saline (n = 7 to 11). (C) IgM levels were measured in the BAL (n = 4 to 6). (D) VE-cadherin phosphorylation in lung homogenates was assessed by Western blot. Representative image. *P < 0.05 versus saline control, #P < 0.05 relative to LPS for (A) to (C) by one-way ANOVA with Tukey post-test; #P < 0.05 relative to LPS by t test for (D). All values represent means ± SEM.
