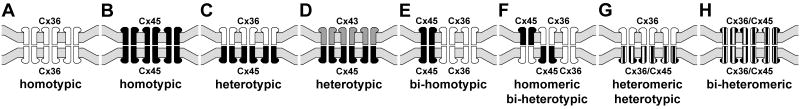
Fig. 4.
Eight generalized connexin/connexon configurations proposed to occur within neuronal gap junctions. A, B, Homomeric homotypic Cx36-to-Cx36 channels (A) and Cx45-to-Cx45 channels (B). C, Cx36 in the upper cell and Cx45 in the lower cell, with Cx36 linking to Cx45 (“homomeric heterotypic”). D, Cx43 in the upper cell and Cx45 in the lower cell, with Cx43 linking to Cx45 (“homomeric heterotypic”). E, Both Cx36 and Cx45 in both cells, with Cx36 linked only to Cx36 and Cx45 linked only to Cx45 (“homomeric bi-homotypic). F, Both Cx36 and Cx45 in both cells, with both connexins on one side linked to both connexins on the other side (“homomeric bi-heterotypic). G, Cx36 only in the upper cells linking to connexons containing a mixture of Cx36/Cx45 in the lower cell (homomeric to heteromeric channels). H, Each connexon contains both Cx36 and Cx45 (heteromeric connexons), linking to heteromeric connexons in the other cell (heteromeric to heteromeric channels).