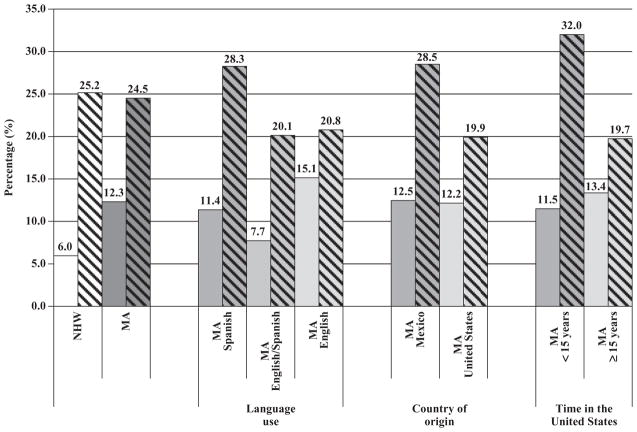
Fig. 1.
Proportion of women who have red blood cell folate concentrations less than 400 ng mL−1 (906 nmol L−1) by race/ethnicity and acculturation and supplement use, National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2007–2010; The value of 400 ng mL−1 (906 nmol L−1) was converted to the NHANES equivalency to be consistent with results reported previously (conversion formula: {[(906 × 0.7876) + 34.2802]/ 2.266} ≥ 330 ng ml−1; unpublished formula from the data presented in Pfeiffer et al., 2011).The banded fill pattern in the figure represent supplement non-users. The Daly et al. value of 400 ng mL−1 (906 nmol L−1) is associated with a birth prevalence rate of neural tube defects of 8 per 10 000 live births; MA, Mexican American; NHW, non-Hispanic white.