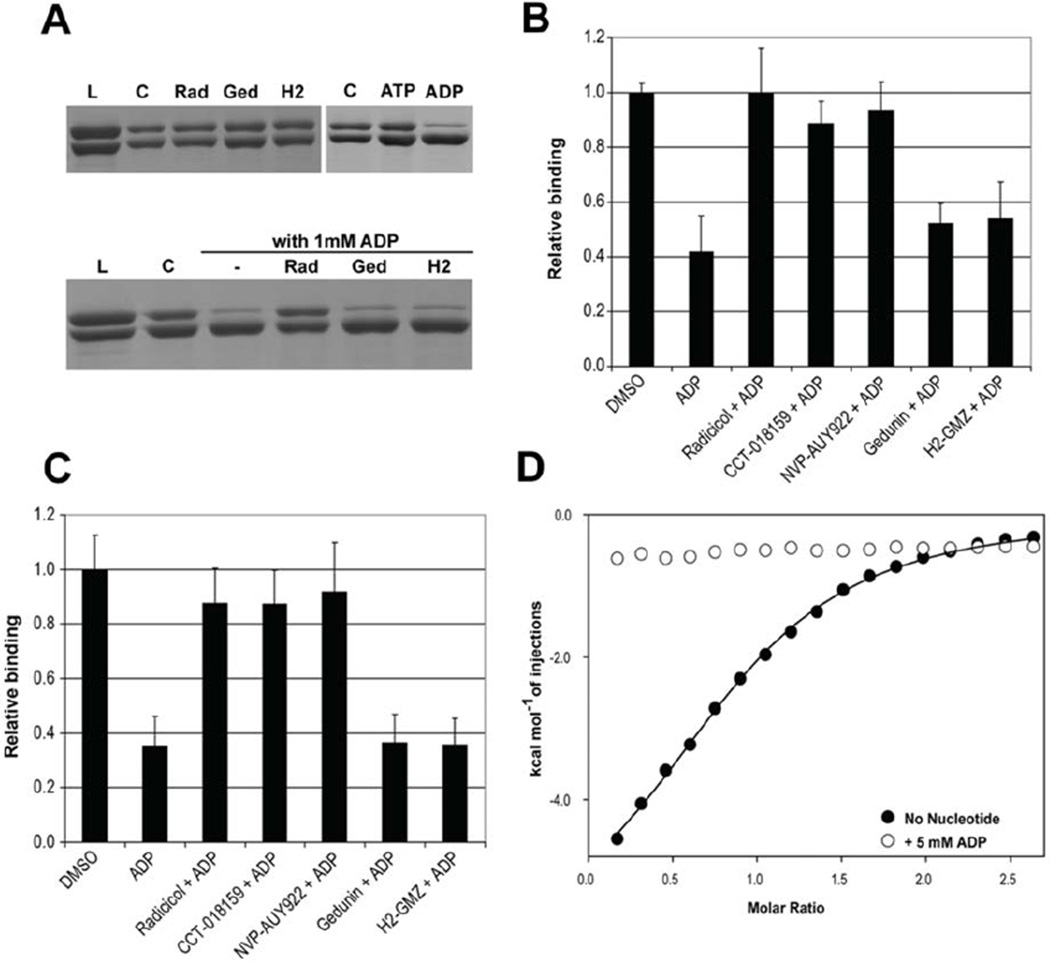
Figure 5.
The PPI inhibitory activity of ADP proceeds through binding to the ATP site of Hsp90. (A) SDS-PAGE of GST pull-down experiments for ΔHsp90β interaction with GST-p50Cdc37. The two proteins were incubated with 1 mM nucleotide or 0.1 mM inhibitor for 15 minutes, loaded onto a GST-affinity column, and eluted with reduced glutathione. The upper gels show elution of a stable complex in the presence of inhibitors or ATP, but the presence of ADP caused disruption of the complex. The bottom gel shows the result of a competition experiment in which the presence of 0.1 mM radicicol protected the complex from ADP, whereas gedunin and H2-GMZ had no effect. L = load, C = control (no ligand), Rad = radicicol, Ged = gedunin, H2 = H2-GMZ. (B, C) Competition experiments for the interaction of ΔHsp90β (B) or ΔHsp90α (C) with p50Cdc37 in the presence of 1 mM ADP and 0.25 mM inhibitors (0.1 mM for gedunin) determined by ELISA. Only ATP site-directed inhibitors protected the complex from ADP. (D) Binding isotherms for the interaction of the N-terminal domain of Hsp90β with p50Cdc37 in the absence and presence of ADP.